37
DESCRIPTIONS
The back panel connections are described as under:
INPUT
(Terminals : 1, 2, 3)
The controller accepts Thermocouples (J, K, T, R, S, B, N & Reserved), 3-wire RTD Pt100 and DC Linear Current / Voltage
(mA/mV/V) as input.
User Manual
neuro 100 96X96
Thermocouple
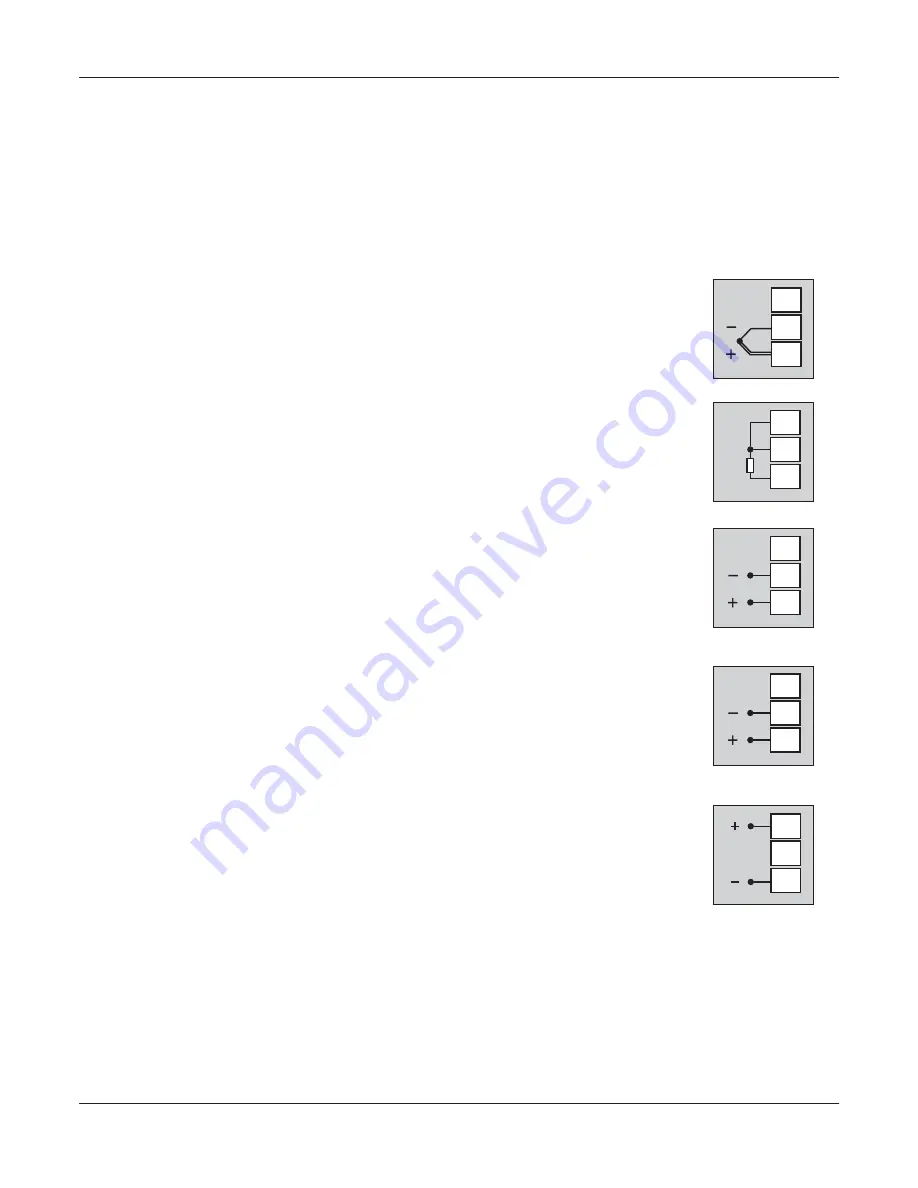
Connect Thermocouple Positive (+) to terminal 1 and Negative (-) to terminal 2 as shown in Figure
3.2 (a). Use the correct type of Thermocouple extension lead wires or compensating cable for the
entire distance ensuring the correct polarity throughout. Avoid joints in the cable.
3
2
1
Figure 3.2 (a)
RTD Pt100, 3-wire
Connect single leaded end of RTD bulb to terminal 1 and the double leaded ends to terminal 2 and 3
(interchangeable) as shown in Figure 3.2 (b).
Use copper conductor leads of very low resistance
ensuring that all 3 leads are of the same gauge and length. Avoid joints in the cable.
3
2
1
Figure 3.2 (b)
DC Linear Voltage (mV / V)
Use a shielded twisted pair with the shield grounded at the signal source for connecting mV / V
source. Connect common (-) to terminal 2 and the signal (+) to terminal 1, as shown in Figure 3.2 (c).
Figure 3.2 (c)
3
2
1
DC Linear Current (mA)
Use a shielded twisted pair with the shield grounded at the signal source for connecting mA source.
Connect common (-) to terminal 2 and the signal (+) to terminal 1, as shown in Figure 3.2 (d).
Make sure that the Jumper Pins for Input selection are shorted using the Shorting-Link (Refer
S
ection 9 Hardware Assembly and Configurations, Input-Jumper Settings).
Figure 3.2 (d)
3
2
1
OUTPUT-1
(Terminals : 4, 6)
DC Linear Current / Voltage Output
The DC Linear (0/4-20 mA) Current or (0-5/10V) Voltage output is also available at Terminal 6 (+)
and Terminal 4 (-) for Retransmission (Recorder) output. Refer Figure 3.3
Figure 3.3
6
5
4
OUTPUT- 2
(Terminals : 7, 8, 9)
OUTPUT- 3
(Terminals : 16, 17, 18)
The Output-2 and Output-3 are available through plug-in modules that can be configured as Relay or SSR through appropriate
Jumper Settings. The connection descriptions are shown in figures 3.4(a) and 3.4(b).




































