6. Patches: Patches (in-depth)
NORD MODULAR G2 V1.1
Page 44
E
E
E
E
D
D
D
DIIIIT
T
T
TIIIIN
N
N
NG
G
G
G
A
A
A
A
M
M
M
MO
O
O
OD
D
D
DU
U
U
UL
L
L
LE
E
E
E
P
P
P
PA
A
A
AR
R
R
RA
A
A
AM
M
M
ME
E
E
ET
T
T
TE
E
E
ER
R
R
R
You can edit the parameters with the mouse. Place the cursor over a knob,
click-hold it (put it in focus) and then move the mouse. The knobs have
no end stops; you may jump from maximum to minimum by turning past
the 6 o’clock position (if Knob control is set to ‘Circular’ in the Setup|Op-
tions dialog box). When a knob is in focus, two small buttons will appear
beneath the knob. Clicking on the ‘up’ button will increase the value one
step for each click and clicking the ‘down’ button will decrease. You can
also use the computer keyboard’s Up/Down arrow keys to increase and de-
crease the focused parameter value. Click on a button to select e.g. a wave-
form button of an oscillator. The selected button will be “depressed”
.
V
V
V
V
O
O
O
OIIIIC
C
C
CE
E
E
E
A
A
A
A
R
R
R
RE
E
E
EA
A
A
A
A
A
A
AN
N
N
ND
D
D
D
FX A
FX A
FX A
FX A
R
R
R
RE
E
E
EA
A
A
A
A Nord Modular G2 Patch can consist of two parts: a polyphonic part and
a monophonic part. In the Editor, these two parts are represented by two sections of the Patch window,
divided by a horizontal split bar. The upper section is called the Voice Area and the lower section the FX
Area. In the Voice Area you place modules that should be duplicated for each voice, e.g. oscillators, en-
velope generators and filters. In the lower Patch window, the FX Area, you can place modules that should
act equally on all voices in the Patch, e.g. different types of FX modules. Modules used in the FX Area
will act on the sum of the signals output from the Voice Area, and consequently will not be duplicated
for each voice in the Patch. This gives two big advantages:
• A module is able to process whole chords, and not just a single voice, affecting the sound the same way
an external audio processor would.
• In most situations you will be able to free up Sound engine power (Patch Load) so you could increase
the polyphony of the Patch.
Cables cannot be connected from modules in one Patch Area to
modules in the other. However, you can route four separate audio
signals from the Voice Area to the FX Area by using the FX In
module. The routing is one-way only; from the Voice Area to the
FX Area. You can also use the four global audio Bus channels to
route audio signals to and from both Patch Areas of all Slots. The
global audio Bus routing is “bidirectional”.
E
E
E
E
X
X
X
XA
A
A
AM
M
M
MP
P
P
PL
L
L
LE
E
E
E
O
O
O
OF
F
F
F
A
A
A
A
P
P
P
P
A
A
A
AT
T
T
TC
C
C
CH
H
H
H
T
T
T
TH
H
H
HA
A
A
AT
T
T
T
U
U
U
US
S
S
SE
E
E
ES
S
S
S
B
B
B
BO
O
O
OT
T
T
TH
H
H
H
T
T
T
TH
H
H
HE
E
E
E
P
P
P
P
O
O
O
OL
L
L
LY
Y
Y
Y
A
A
A
AN
N
N
ND
D
D
D
FX A
FX A
FX A
FX A
R
R
R
RE
E
E
EA
A
A
AS
S
S
S
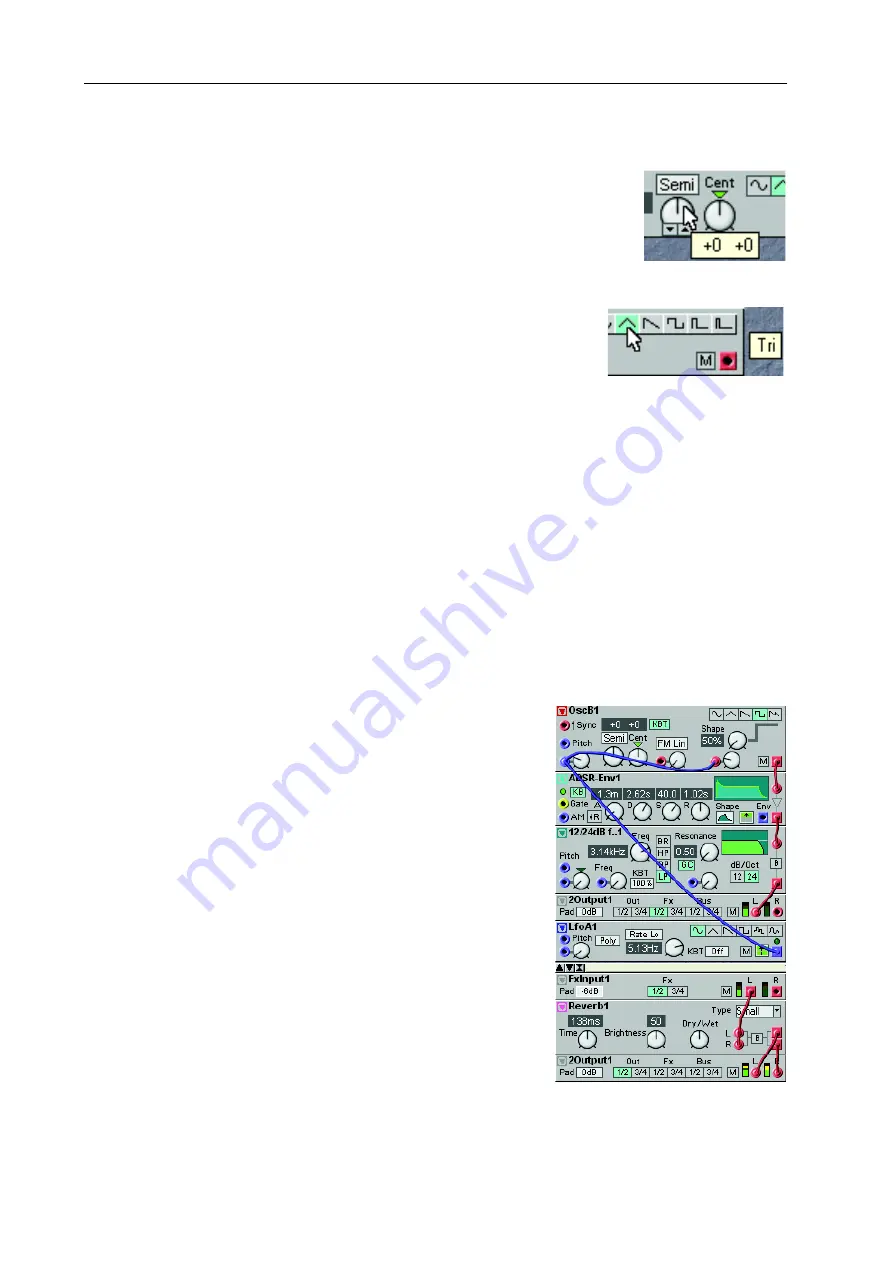
This example shows a Patch where both the Poly and FX Areas are
used:
The ‘2-Out1’ module in the Voice Area is set to route the signal
to FX In 1/2, the Left and Right output of the ‘FX In1’ module
in the FX Area. The sum of all voices from the Voice Area is sent
to the FX Area to be processed in the ‘Reverb1’ module and out-
put at
O
UT
1
and
O
UT
2
jack of the synthesizer.
A Patch in the Voice Area set to ‘Mono’ in the Voice Mode dis-
play box would give the same result as having the Patch only in
the FX Area instead.
Editing a knob
Editing a button






























