Advanced Settings
74
N150 2-Port Wireless Router WNR612v3
To set up Dynamic DNS:
1.
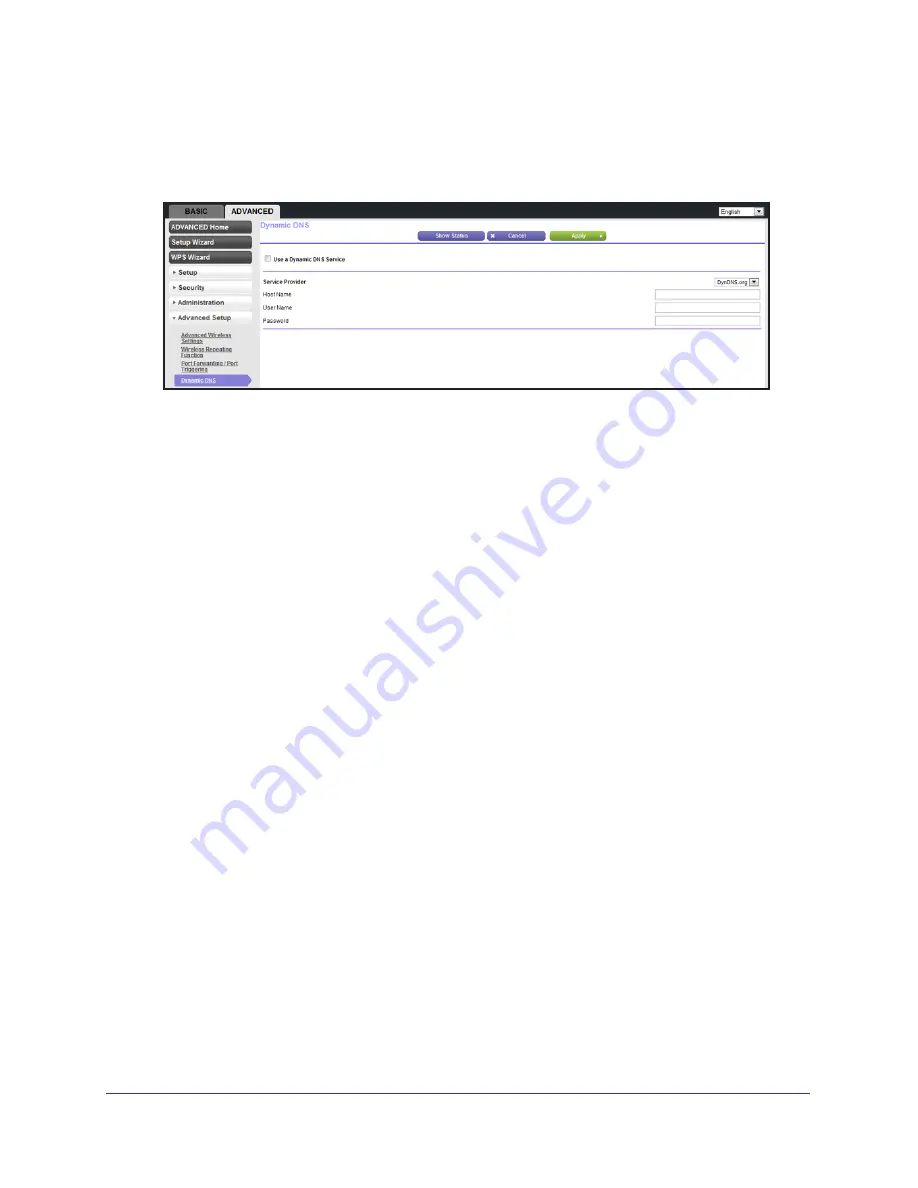
On the Advanced tab, select
Advanced Setup > Dynamic DNS
to display the following
screen:
2.
Register for an account with one of the Dynamic DNS service providers whose names
appear in the Service Provider list. For example, for DynDNS.org, select
www.dyndns.org
.
3.
Select the
Use a Dynamic DNS Service
check box.
4.
Select the name of your Dynamic DNS service provider.
5.
Type the host name (or domain name) that your Dynamic DNS service provider gave you.
6.
Type the user name for your Dynamic DNS account. This is the name that you use to log in
to your account, not your host name.
7.
Type the password (or key) for your Dynamic DNS account.
8.
If your Dynamic DNS provider allows the use of wildcards in resolving your URL, you can
select the
Use Wildcards
check box to activate this feature.
For example, the wildcard feature causes
*.yourhost.dyndns.org
to be aliased to the
same IP address as yourhost.dyndns.org.
9.
Click
Apply
to save your configuration.
Static Routes
Static routes provide additional routing information to your router. Typically, you do not need
to add static routes. You have to configure static routes only for unusual cases such as
multiple routers or multiple IP subnets on your network.
As an example of when a static route is needed, consider the following case:
•
Your primary Internet access is through a cable modem to an ISP.
•
You have an ISDN router on your home network for connecting to the company where
you are employed. This router’s address on your LAN is 192.168.1.100.
•
Your company’s network address is 134.177.0.0.
When you first configured your router, two implicit static routes were created. A default route
was created with your ISP as the gateway, and a second static route was created to your
local network for all 192.168.1.x addresses. With this configuration, if you attempt to access a
device on the 134.177.0.0 network, your router forwards your request to the ISP. The ISP






























