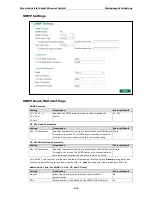
Moxa Industrial Smart Ethernet Switch
The STP/RSTP Concept
A-3
•
Each port has a cost that specifies the efficiency of each link. The efficiency cost is usually determined by
the bandwidth of the link, with less efficient links assigned a higher cost.
STP Calculation
The first step of the STP process is to perform calculations. During this stage, each bridge on the network
transmits BPDUs. The following items will be calculated:
•
Which bridge should be the Root Bridge. The Root Bridge is the central reference point from which the
network is configured.
•
The Root Path Costs for each bridge. This is the cost of the paths from each bridge to the Root Bridge.
•
The identity of each bridge’s Root Port. The Root Port is the port on the bridge that connects to the Root
Bridge via the most efficient path. In other words, the port connected to the Root Bridge via the path with
the lowest Root Path Cost. The Root Bridge, however, does not have a Root Port.
•
The identity of the Designated Bridge for each LAN segment. The Designated Bridge is the bridge with the
lowest Root Path Cost from that segment. If several bridges have the same Root Path Cost, the one with the
lowest Bridge Identifier becomes the Designated Bridge. Traffic transmitted in the direction of the Root
Bridge will flow through the Designated Bridge. The port on this bridge that connects to the segment is
called the Designated Bridge Port.
STP Configuration
After all of the bridges on the network agree on the identity of the Root Bridge, and all other relevant
parameters have been established, each bridge is configured to forward traffic only between its Root Port and
the Designated Bridge Ports for the respective network segments. All other ports are blocked, which means
that they will not be allowed to receive or forward traffic.
STP Reconfiguration
Once the network topology has stabilized, each bridge listens for Hello BPDUs transmitted from the Root Bridge
at regular intervals. If a bridge does not receive a Hello BPDU after a certain interval (the Max Age time), the
bridge assumes that the Root Bridge, or a link between itself and the Root Bridge, has ceased to function. This
will trigger the bridge to reconfigure the network to account for the change. If you have configured an SNMP
trap destination, the first bridge to detect the change will send out an SNMP trap when the topology of your
network changes.
Differences between STP and RSTP
RSTP is similar to STP, but includes additional information in the BPDUs that allow each bridge to confirm that
it has taken action to prevent loops from forming when it decides to enable a link to a neighboring bridge.
Adjacent bridges connected via point-to-point links will be able to enable a link without waiting to ensure that
all other bridges in the network have had time to react to the change. The main benefit of RSTP is that the
configuration decision is made locally rather than network-wide, allowing RSTP to carry out automatic
configuration and restore a link faster than STP.