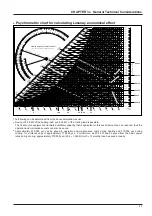
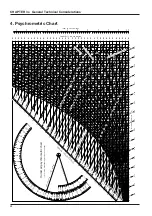
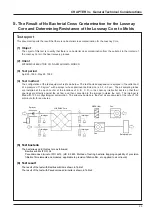
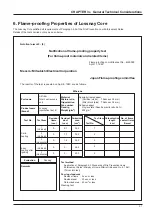
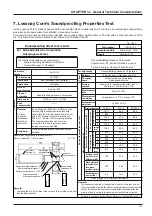
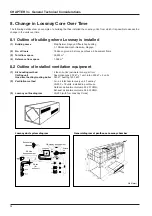
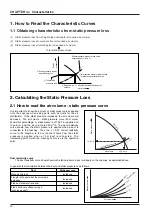
37
CHAPTER 3
●
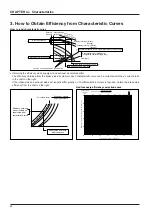
General Technical Considerations
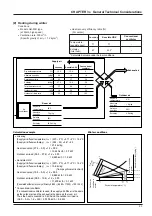
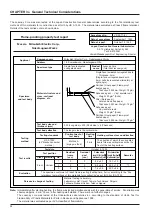
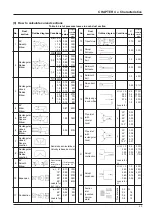
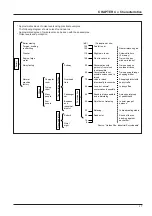
9.2 Comparison of static-type and rotary-type heat recovery units
Item
Construction/
principle
Moving parts
Material quality
Mounting of prefilter
Element clogging
Air leakage
Gas transmission
rate
Bacteria
transmission rate
Operation during
off-seasons
Maintenance
Life
Model system and
comparison
Standard treatment
air volume
Enthalpy recovery
efficiency
Pressure loss
Installation space
(W
×
D
×
H)(mm)
Static-type
<Conductive transmission-type: cross-flow>
Static-type transmission total heat recovery unit
with orthogonally layered honeycomb shaped
treated paper formed into multiple layers.
●
As the supply air and exhaust air pass through
different passages (sequentially layered), the air
passages are completely separated.
●
None
Fixed core
Treated paper
Required (periodic cleaning required)
●
Occurs (state where dirt adheres onto element air
passage surface. However, this is easily removed
with a vacuum cleaner.)
Approximately 2.5% air leak at standard fan
position.
Leaks on the air supply side can be reduced to 0 by
leaking the loss air volume (approx. 10%) on the
exhaust side with the fan position to the core.
●
Gas transmission ( Ammonia
: 28%,
hydrogen sulfide : approx. 6.7%)
●
Low (As air intake/exhaust are separate,
transmission is low.)
Bypass circuit required (SA pass or RA pass only)
Core cleaning: More than once (every two years)
The core surface will clog with lint and dirt, but
cleaning is easy with a vacuum cleaner.
Only the two core air passage intakes need to be
cleaned.
Core: Semi-permanent (10 years or more)
(The static-type does not break.)
o
Available from small to large.
Example
o
Characteristic design of small
LU-1605
and medium models possible.
Large models are easy to
match to machine room layout.
40 to 25,000 m
3
/h
8,000 m
3
/h
Temperature:77%
Enthalpy
Heating : 71%
Cooling : 66%
170 Pa
Effective for small to medium capacity
600
×
2100
×
2540
(Layout is free according to combination.)
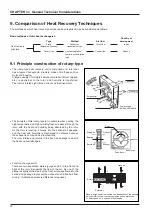
Rotary-type
<Heat accumulation/humidity accumulation-
type: counterflow>
The rotor core is composed of honeycomb-shaped
kraft paper, etc., to which a moisture absorbent is
applied (lithium chloride, etc.). This rotor is rotated,
and heat accumulation/humidity accumulation -
heat discharge/humidity discharge of total heat
exchange is performed by passing the exhaust and
intake airs into a honeycomb passage.
×
Supply air and exhaust airs flow into the same air
passage because of the rotary-type construction.
×
Used (rotor driven with belt by gear motor)
Rotor core (8rpm)
Treated paper, aluminum plates, etc.
Required (periodic cleaning required)
×
Occurs (Dust is smeared into element air passage filter.)
(The dust adhered onto the core surface is smeared
into the air passage by the purge sector packing.
Thus, it cannot be removed easily and the air
volume decreases.)
×
Purged air volume occurs
To prevent leakage of exhaust to the air intake side, a
purge air volume (6 to 14%) leak is created to the
exhaust side. Thus, there are problems in the purge
sector operation conditions (pressure difference,
speed), and the air volume balance must be balanced.
×
Gas transmission (Ammonia
: 45-57%,
hydrogen sulfide : approx. 3.2-4%)
×
High (As air intake/exhaust are the same,
transmission is high.)
Bypass circuit required (Required on both air intake
and exhaust air outlet sides)
(In theory, operation is possible by stopping the
rotation, but the core will over-absorb, causing rainage.)
Core cleaning: Once every one or two years
Cleaning is difficult as dust is smeared into core
with the packing.
×
Gear motor for rotor drive
: Periodic inspection
×
Rotor bearing, rotor drive belt : Periodic inspection
Core: Semi-permanent (10 years or more)
(Periodic replacement is required according to the
rotor bearings and core clogging.)
×
Rotor drive belt
: Periodic replacement
×
Drive motor, rotor bearing : Periodic replacement
Large type only
Example
×
Small models are difficult to
EV-1500
design because of the rotor
magnitude.
o
100 to 63,000 m
3
/h
8,000 m
3
/h
74%
180 Pa
Large capacity models are
320
×
1700
×
1700
effective
Measure of useability
●
High
o
Average
×
Poor
Содержание Lossnay PZ-41SLB-E
Страница 4: ...CHAPTER 1 Ventilation for Healthy Living Lossnay Unit ...
Страница 17: ......
Страница 18: ...CHAPTER 2 Lossnay Construction and Principle ...
Страница 24: ...CHAPTER 3 General Technical Considerations ...
Страница 41: ......
Страница 42: ...CHAPTER 4 Characteristics ...
Страница 56: ...53 CHAPTER 4 Characteristics ...
Страница 57: ...54 CHAPTER 4 Characteristics ...
Страница 59: ......
Страница 60: ...CHAPTER 5 System Design Recommendations ...
Страница 68: ...CHAPTER 6 Examples of Lossnay Applications ...
Страница 83: ......
Страница 84: ...CHAPTER 7 Installation Considerations ...
Страница 88: ...CHAPTER 8 Filtering for Freshness ...
Страница 96: ...CHAPTER 9 Service Life and Maintenance ...
Страница 98: ...CHAPTER 10 Ventilation Standards in Each Country ...
Страница 101: ......
Страница 102: ...CHAPTER 11 Lossnay Q and A ...
Страница 108: ...Lossnay Remote Controller ...
Страница 109: ......
Страница 197: ...MEMO ...
Страница 198: ...Y04 002 Jul 2004 MEE ...