33
KPS-MT50 • Digital multimeter
ENG
Voltage is the difference in electrical potential between two points.
The polarity of ac (alternating current) voltage varies over time; the polarity of
dc (direct current) voltage is constant.
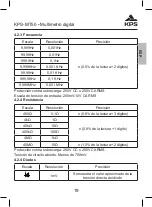
The Meter’s DC voltage ranges are 400.0mV, 4.000V, 40.00V, 400.0V and
1000V; AC voltage ranges are 400.0mV(only in range mode), 4.000V, 40.00V,
400.0V and 750V.
To measure ac or dc voltage:
1. Set rotary switch to the
V position.
2 Connect the black test leader and red test leader to the COM and V terminals
respectively.
3. Connect the test leader to the circuit being measured
4. Read the displayed value. The polarity of red test lead connection will be
indicated when making a DCV measurement.
3.2.2 2 Resistance measurement
Resistance is an opposition to current flow.
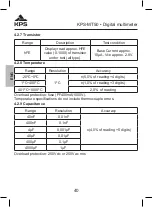
The Meter’s resistance ranges are 400,0Ω, 4,000kΩ, 40,00kΩ, 400,0kΩ,
4,000MΩ y 40,00MΩ.
To measure resistance:
1 Set the rotary switch to
position.
2 Connect the black and red test leads to the COM and Ω terminals respectively.
3. Connect the test leads to the circuit being measured and read the displayed
value.
Some tips for measuring resistance:
- The measured value of a resistor in a circuit is often different from the
resistor’s rated value. This is because the Meter’s test current flows through
all possible paths between the probe tips.
- In order to ensure the best accuracy in measurement of low resistance, short
the test leads before measurement and memory the test probe resistance in
mind. This necessary to subtract for the resistance of the test leads.
- On 40MΩ range, the meter may take a few seconds to stabilize reading. This
is normal for high resistance measuring.
- When the input is not connected, i.e. at open circuit, the figure “OL” will be
displayed for the overrange condition