2
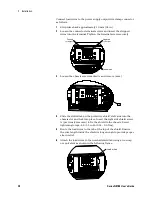
Installation
32
Series N8700 User’s Guide
Output Noise and Impedance Effects
To minimize the noise pickup or radiation, the load wires and remote
sense wires should be twisted-pairs to the shortest possible length.
Shielding of sense leads may be necessary in high noise
environments. Where shielding is used, connect the shield to the
chassis via a rear panel ground screw. Even if noise is not a concern,
the load and remote sense wires should be twisted-pairs to reduce
coupling, which might impact the stability of power supply. The sense
leads should be separated from the power leads.
Twisting the load wires reduces the parasitic inductance of the cable,
which could produce high frequency voltage spikes at the load and
the output because of current variation in the load itself.
The impedance introduced between the power supply output and the
load could make the ripple and noise at the load worse than the noise
at the power supply rear panel output. Additional filtering with
bypass capacitors at the load terminals may be required to bypass the
high frequency load current.
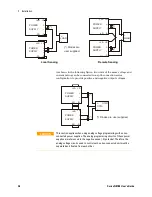
Inductive Loads
Inductive loads can produce voltage spikes that may be harmful to
the power supply. A diode should be connected across the output.
The diode voltage and current rating should be greater than the
power supply maximum output voltage and current rating. Connect
the cathode to the positive output and the anode to the negative
output of the power supply.
Where positive load transients such as back EMF from a motor may
occur, connect a surge suppressor across the output to protect the
power supply. The breakdown voltage rating of the suppressor must
be approximately 10% higher than the maximum output voltage of the
power supply.
Battery Charging
CAUTION
If a battery or external voltage source is connected across the output and the
output is programmed below the battery or external voltage source, the power
supply will continuously sink current from the external source. This could
damage the power supply.
To avoid damaging the power supply, insert a reverse blocking diode
in series with the + output connection of the power supply. Connect
the diode’s cathode to the + battery terminal or external voltage
source. Connect the diode’s anode to the + output terminal of the
power supply.