35
EN2R-9031 0402R15-NE
SYSTEM OPERATION
S4565AF, BF, CF, DF, EF, PF, QF, RF, TF
General
Lock-out reset
The S4565AF, BF, CF, DF, EF, PF, QF, RF and TF ignition
controls can be reset by either depressing the internal/
external reset button (suffix AF, BF, CF and DF) or by
interrupting the permanent life (suffix PF, QF, RF, and TF). If a
first reset is not succesful, wait at least 15 seconds before
attempting another one.
NOTE 15.: When first starting, the ignition control can be in
the lock-out condition; reset the ignition control.
NOTE 16.: If during normal use the reset button is pressed,
the gas valves close and the ignition control
starts a new sequence after releasing the reset
button.
NOTE 17.: If permanent alarm output:neon indicator with
integral resistor >150 k
Ω (
max 1 mA)
NOTE 18.: If an external LPG valve and gas pressure switch
are connected, the LPG valve is energized after
call for heat. The ignition control stays in waiting
mode untill the gas pressure switch is closed. If
during normal operation gas pressure switch
opens, the gas valves will not be closed.
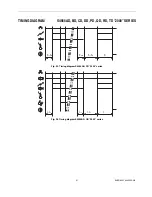
Suffix AF and PF (see Fig. 41.)
When there is a call for heat a self check period (T
c
) plus a
waiting period (T
w
) elapse before built-in igniter and gas valve
are switched on.
The ignition spark ignites gas and resulting flame is detected
by the flame rod.
After flame establishment a predetermined, extended ignition
time can be included.
If flame is not established within the safety time (T
s
), the
ignition control locks out.
If the flame is lost during normal run, the ignition control
repeats start sequence.
Suffix BF and QF (see Fig. 42.)
When there is a call for heat a self check period (T
c
) plus a
waiting period (T
w
) elapse before built-in igniter and pilot gas
valve are switched on.
The ignition spark ignites pilot gas and resulting flame is
detected by the flame rod.
After flame establishment a predetermined, extended ignition
time can be included then the main valve is switched on.
If flame is not established within the safety time (T
s
), the
ignition control locks out.
If the flame is lost during normal run, the ignition control
repeats start sequence.
Suffix CF and RF (see Fig. 43.
When there is a call for heat the fan starts running through
the no air position of the air proving switch after a self check
period (T
c
) plus a waiting period (T
w
).
When sufficient air flow is proven by the air proving switch,
the built-in igniter and gas valve are switched on.
The ignition spark ignites gas and resulting flame is detected
by the flame rod.
After flame establishment a predetermined, extended ignition
time can be included.
If flame is not established within the safety time (T
s
), the
ignition control locks out.
If the flame is lost during normal run, the ignition control
repeats start sequence.
If no air is proven by the air proving switch within the safety
time (T
s
), the ignition control locks out.
Suffix DF and TF (see Fig. 44.)
When there is a call for heat the fan starts running through
the no air position of the air proving switch after a self check
period (T
c
) plus a waiting period (T
w*
).
When sufficient air flow is proven by the air proving switch,
the built-in igniter and pilot gas valve are switched on.
The ignition spark ignites pilot gas and resulting flame is
detected by the flame rod.
Ignition is switched off after a predetermined extended
ignition time T(
ext
) and flame establishment and then the
main valve is switched on.
If flame is not established within the safety time (T
s
), the
ignition control locks out.
If the flame is lost during normal run, the ignition control
repeats start sequence.
If no air is proven by the air proving switch within the safety
time (T
s
), the ignition control locks out.
* The safety time starts after fan is switched on.