Rev. 1.00
140
��ne ��� �01�
Rev. 1.00
141
��ne ��� �01�
HT66FM5440
Brushless DC Motor A/D Flash MCU
HT66FM5440
Brushless DC Motor A/D Flash MCU
I
2
C Interface
The I
2
C interface is used to communicate with external peripheral devices such as sensors,
EEPROM memory etc. Originally developed by Philips, it is a two line low speed serial interface
for synchronous serial data transfer. The advantage of only two lines for communication, relatively
simple communication protocol and the ability to accommodate multiple devices on the same bus
has made it an extremely popular interface type for many applications.
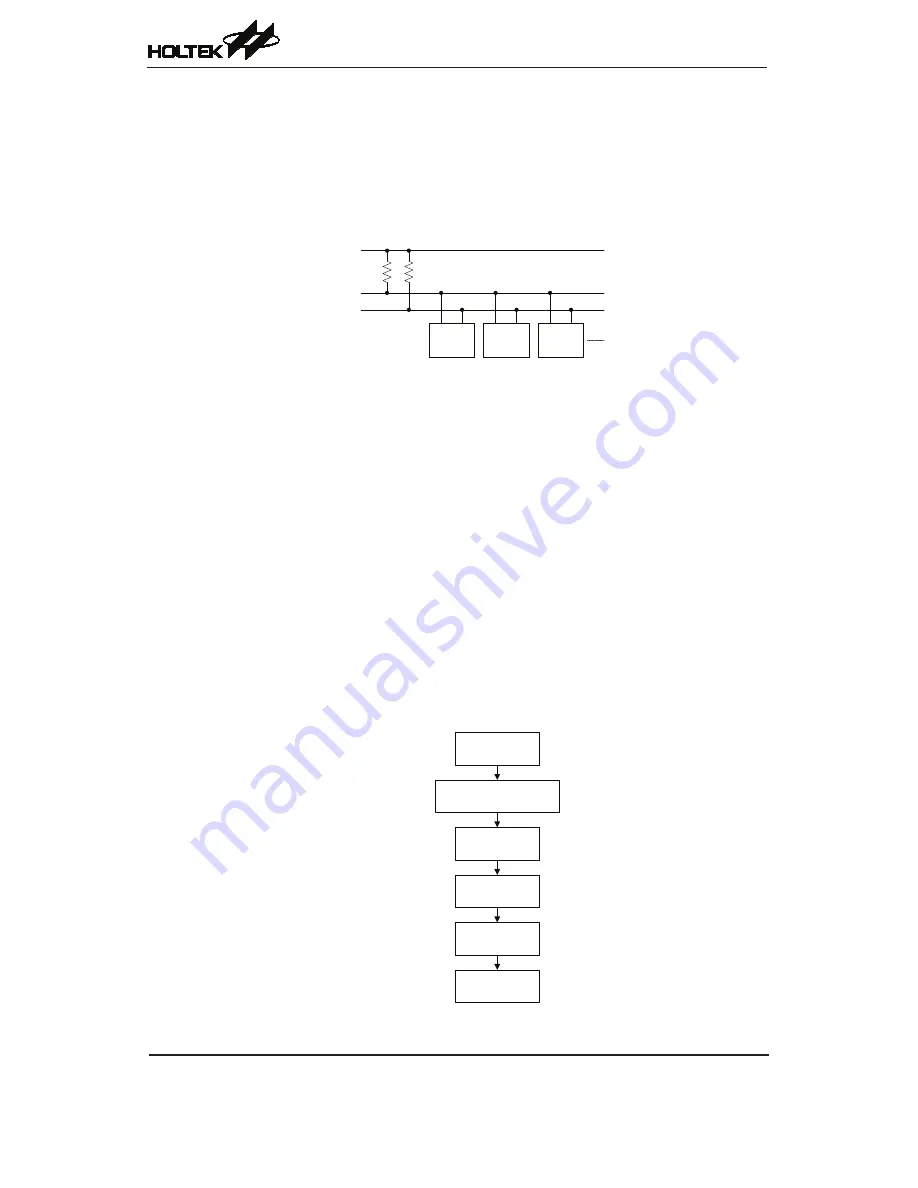
Device
Slave
Device
Master
Device
Slave
VDD
SDA
SCL
I
2
C Master/Slave Bus Connection
I
2
C Interface Operation
The I
2
C serial interface is a two line interface, a serial data line, SDA, and serial clock line, SCL. As
many devices may be connected together on the same bus, their outputs are both open drain types.
For this reason it is necessary that external pull-high resistors are connected to these outputs. Note
that no chip select line exists, as each device on the I
2
C bus is identified by a unique address which
will be transmitted and received on the I
2
C bus.
When two devices communicate with each other on the bidirectional I
2
C bus, one is known as the
master device and one as the slave device. Both master and slave can transmit and receive data,
however, it is the master device that has overall control of the bus. For this device, which only
operates in slave mode, there are two methods of transferring data on the I
2
C bus, the slave transmit
mode and the slave receive mode.
It is suggested that the user should not allow the device to enter IDLE or SLEEP mode by
application program during processing I
2
C communication.
If the pin is configured to SDA or SCL function of I
2
C interface, the pin is configured to open-collect
Input/Output port and its Pull-high function can be enabled by programming the related Generic
Pull-high Control Register.
START signal
from Master
Send slave address
and R/W bit from Master
Acknowledge
from slave
Send data byte
from Master
Acknowledge
from slave
STOP signal
from Master
















































