12
EPSON
S5U1C63000H2 MANUAL
(S1C63 FAMILY IN-CIRCUIT EMULATOR)
CHAPTER 5: OPERATION AND FUNCTION OF S5U1C63000H2
5.2 Break Function
●
Forced break
The debugger on the host machine can forced break the emulation. This function is useful when the
program counter does not proceed by executing the SLP or HALT instruction in a single step process.
●
Break commands
Some break commands are available to set various breaking conditions. A break occurs when the
break condition specified by the command and status of the S1C63000 CPU are met.
●
Break by accessing to undefined area
This break occurs when the target program accesses an address exceeding the ROM capacity of the
actual chip. The break is also occurred when any address other than the RAM area or mapped I/O
area of the actual chip is accessed.
●
Break by accessing write protect area
This break occurs when the target program writes data to the read only memory such as a character
generator ROM. The memory contents are protected even this break occurs.
●
Break by incorrect stack accessing
This break occurs when the target program makes incorrectly stacking operation exceeding the
defined stack area in the S1C63000 CPU.
●
BRKIN terminal
When a signal is input to the BRKIN terminal, a break occurs at the falling edge of the signal.
5.3 Monitoring Terminals
●
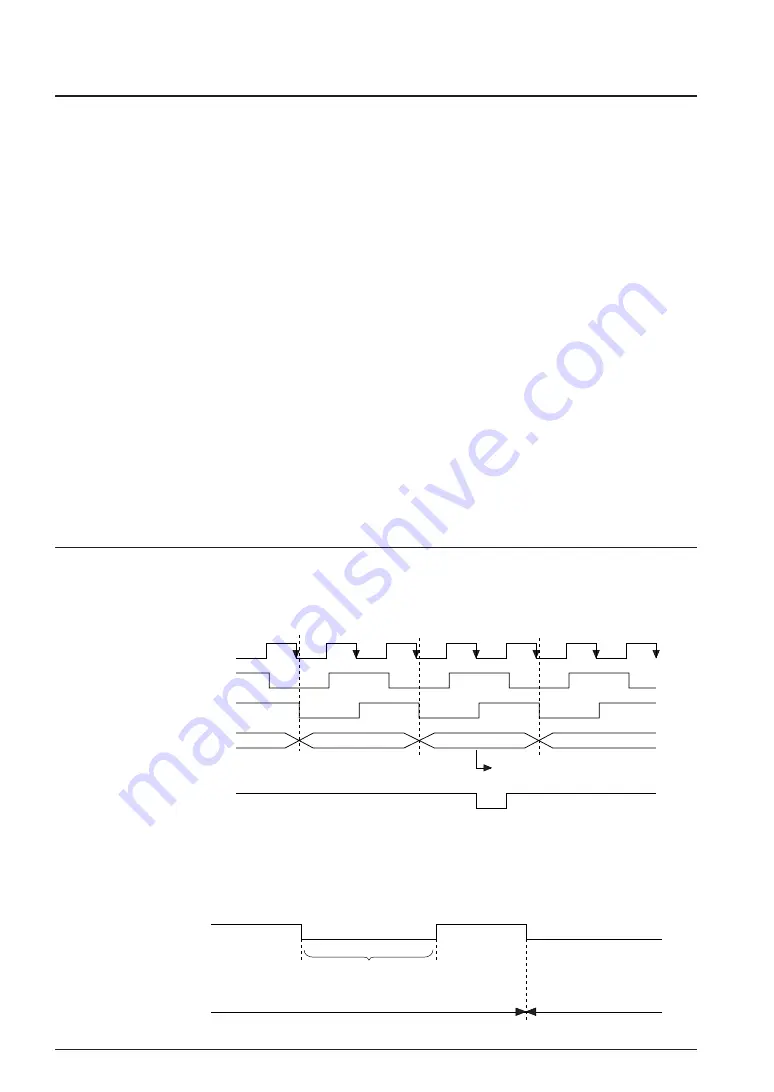
TRGOUT output terminal
A low level pulse is output at the T3 state of the clock when the trace trigger condition and the bus
cycle are met.
T1
T2
T3
T4
PK
PL
Bus cycle
TRGOUT output
CLK from
peripheral circuit board
Coincidence with trace trigger
Fig. 5.3.1 TRGOUT terminal output
●
STOPOUT output terminal
A low level is output when the S1C63000 CPU is suspended (by execution of the HALT or SLP
instructions). This terminal also outputs low level during break.
Indicating suspension
of CPU operation
STOPOUT output
Running
Breaking
Fig. 5.3.2 STOPOUT terminal output
















































