The Switch User’s Guide
5.3 Redundancy
5.3.1 Spanning Tree
1. Spanning Tree Protocol
The IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol allows for the blocking of links between
switches that form loops within the network. When multiple links between switches
are detected, a primary link is established. Duplicated links are blocked from use
and become standby links. The protocol allows for the duplicate links to be used in
the event of a failure of the primary link. Once the Spanning Tree Protocol is
configured and enabled, primary links are established and duplicated links are
blocked automatically. The reactivation of the blocked links (at the time of a primary
link failure) is also accomplished automatically without operator intervention.
This automatic network reconfiguration provides maximum uptime to network users.
However, the concepts of the Spanning Tree Algorithm and protocol are a
complicated and complex subject and must be fully researched and understood. It is
possible to cause serious degradation of the performance of the network if the
Spanning Tree is incorrectly configured. Please read the following before making
any changes from the default values.
The Switch STP performs the following functions:
z
Creates a single spanning tree from any combination of switching or bridging
elements.
z
Creates multiple spanning trees – from any combination of ports contained
within a single switch, in user specified groups.
z
Automatically reconfigures the spanning tree to compensate for the failure,
addition, or removal of any element in the tree.
z
Reconfigures the spanning tree without operator intervention.
Bridge Protocol Data Units
For STP to arrive at a stable network topology, the following information is used:
z
The unique switch identifier
z
The path cost to the root associated with each switch port
z
The port identifier
STP communicates between switches on the network using
Bridge Protocol Data
Units (BPDUs)
.
Each BPDU contains the following information:
z
The unique identifier of the switch that the transmitting switch currently believes
is the root switch
z
The path cost to the root from the transmitting port
z
The port identifier of the transmitting port
The switch sends BPDUs to communicate and construct the spanning-tree topology.
All switches connected to the LAN on which the packet is transmitted will receive the
BPDU. BPDUs are not directly forwarded by the switch, but the receiving switch
uses the information in the frame to calculate a BPDU, and, if the topology changes,
initiates a BPDU transmission.
The communication between switches via BPDUs results in the following:
35
Содержание ESW-8228
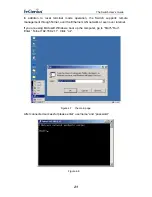
Страница 22: ...The Switch User s Guide NOTICE The factory default User name is guest Pass word is guest 22...
Страница 34: ...The Switch User s Guide Figure 5 19 34...
Страница 49: ...The Switch User s Guide 49...
Страница 53: ...The Switch User s Guide Figure 5 33 2 Choose port2 to enter into VLAN configuration The default PVID is 1 53...
Страница 54: ...The Switch User s Guide Figure 5 34 54...