Operating modes and functions
ELSA LANCOM DSL/10 Office
25
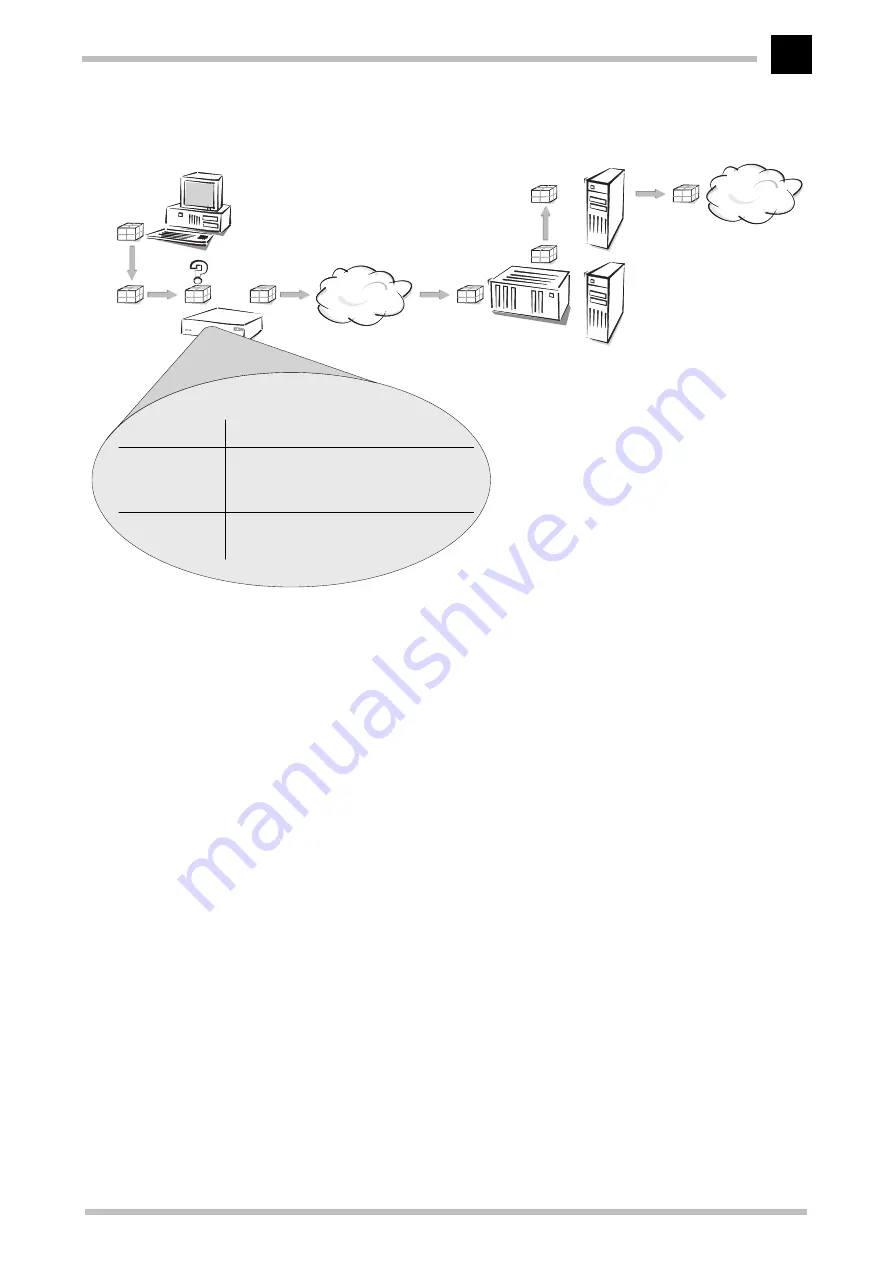
A simplified example will clarify this process.
A data packet from a computer initially finds the path to the Internet through the
IP address of the receiver. The computer sends the packet with this address over the LAN
to the router. The router uses the IP address first to check the IP routing table and finds
the remote station to which this address belongs (e.g. 'Provider_A'). The router then uses
this name to check the name list and finds the name of the associated access
concentrators (AC) and the service that should be used with this AC. The router also
obtains the user name and password required for login to Provider A from the PPP list.
The router can then establish a connection on the xDSL line and indicate that it wants a
connection to the access concentrator of Provider A and to use Service X there. Once the
connection has been established, the router can forward the data packet to the Internet
over the xDSL line.
You will find additional information on IP networks etc. in the technical documentation.
The following sections introduce the names and PPP list and briefly describe the
parameters they contain, describe their connections to other lists and their parameters,
and how they are configured in the software.
For further information on the IP routing table, see the 'IP routing' section.
Internet
ADSL
Access Concentrator
Provider A, Service X
Access Concentrator
Provider B
Switching center
Internet user's PC
Router
Data packet
with
IP address
IP routing tab.
IP address
➮
name of remote station
Name-list
Remote station
➮
access
concentrator
and service
PPP-list
Remote station
➮
user name and
password
Содержание Lancom DSL/10 Office
Страница 1: ...M ELSA LANCOM TM DSL 10 Office 20554 0200...
Страница 4: ......
Страница 8: ...Contents ELSA LANCOM DSL 10 Office VIII...
Страница 48: ...Operating modes and functions ELSA LANCOM DSL 10 Office 40...
Страница 106: ...Description of the menu options ELSA LANCOM DSL 10 Office R50...






























