Project 32
Light Bulb with Meter
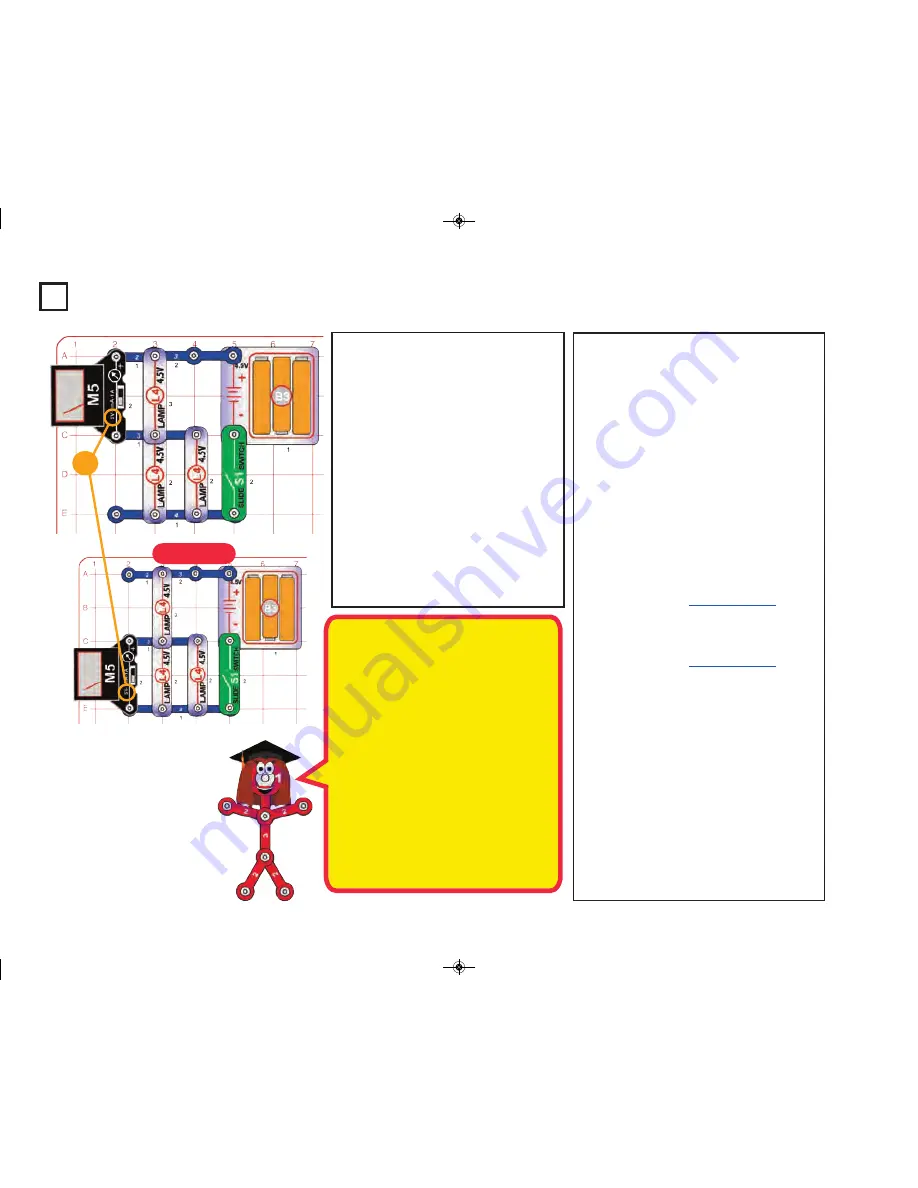
This circuit is like the preceding one, but
adds a meter so you can compare the volt-
ages across the lamps. Build the circuit, set
the meter (M5) to the 5V setting, and turn on
the slide switch (S1). The meter measures
the voltage across the top lamp, which is
bright.
Part B:
Move the meter so it is across the
lower lamps, as shown. Now the meter meas-
ure the voltage across the lower lamps, which
are very dim. Watch the lower lamps and the
meter closely; initially the lamps are dark, but
slowly become dimly lit.
Note:
The voltage in Part B will be much
smaller; in some cases it may even be too
small to measure with your M5 meter. M5
is a simple meter, don’t expect it to be as ac-
curate as normal electronic test instruments.
Part B
What is the voltage across the top lamp?
What is the voltage across the lower lamps?
Remove the top 3-snap wire (which connects
to the battery holder) and place the meter
there. Set the meter to the 1A setting and
measure the circuit current.
With the above measurements, use Ohm’s Law
( ) to calculate the resistance of the lamps:
Find a fluorescent or LED bulb and feel the heat
coming off it; you won’t feel much. Find an incan-
descent lamp THAT HAS BEEN OFF FOR A
WHILE and turn it on. Feel the heat it produces;
it soon becomes too hot to touch. How much hot-
ter is the incandescent bulb?
5V
The resistance of the lower lamps is typically
about triple that of the top lamp, but your re-
sults may vary. All wires have higher resist-
ance when they are very hot.
Incandescent bulbs produce lots of heat, and
the glass bulb prevents the filament from react-
ing with oxygen in the air and burning. When
the voltage rating of an incandescent bulb is ex-
ceeded, the filament gets so hot it burns out.
Filaments are usually made of tungsten, since
ordinary copper would melt.
Most of the electrical energy used by incan-
descent light bulbs becomes heat, not light.
Only about 5% of the electricity used by incan-
descent bulbs is converted into light. Without
the more efficient fluorescent bulbs (and in-
creasingly LEDs bulbs), our society of office
buildings might have been much different.
Resistance
(top lamp)
=
Voltage
(top lamp)
Current
(as measured)
Resistance
(each lower lamp)
=
Voltage
(lower lamps)
half of Current
(since split between 2 lamps)
=
=
-37-
SC_STEM1_manual_PRINT.qxp_Layout 1 7/13/17 4:43 PM Page 38
















































