SOI/TD 2005-2 PR
/26
599 36 83-66
14
-
a thermostat with a thermal fuse (206ºC)
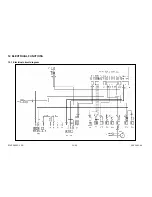
The temperature of the water is controlled by the main circuit board via an NTC sensor (ST) which is
connected to connectors H1-H3.
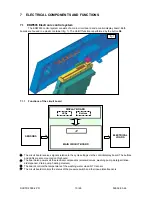
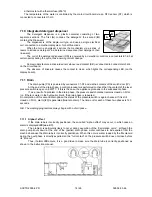
7.10 Integrated detergent dispenser
The detergent dispenser is a plastic container consisting of two
separate sections. The first (
A
) contains the detergent; the second (
B
)
contains the Rinse-aid.
The dispenser is of the single-coil type, and uses a single electrical
coil, connected to a mechanical system, for both functions.
When the coil is energized, it actions the mechanism via a series of
levers to introduce detergent in a determined sequence (first detergent, then
rinse-aid).
The coil of the detergent dispenser (DD) is powered by an electronic control via connectors E1-E3 at
certain points during the cycle, thus ensuring correct dosage.
Some models feature a rinse-aid sensor whose reed contact (SB) is connected to connectors G3-G4
on the circuit board.
The absence of rinse-aid causes the contact to close, which lights the corresponding LED (on the
display board).
7.11 Drain
The drain pump (PS) is powered by connectors C1-D1 and via the contacts of the switch door (IP).
At the end of the drain phase, a control procedure is performed to check that the contact of the level
pressure switch is open on EMPTY. If this is the case, the appliance proceeds to the subsequent phase.
If, as a result of a problem in the drain phase, the pressure switch contact remains closed on FULL
(i.e. if there is water in the hydraulic circuit), the drain phase is repeated.
On completion of this second drain phase, the status of the pressure switch is again checked. If it is still
closed on FULL, alarm [i20] is generated (failure to drain). The time-out for each of these two phases is 120
seconds.
N.B. The washing programmes always begin with a drain phase.
7.11.1 Siphon” effect
If the drain tube is incorrectly positioned, the so-called “siphon effect” may occur, in which case an
alarm is displayed
iF0 (see 9.1).
The problem is particularly likely to occur during execution of the “declaration cycle”: although the
drain pump shuts down at the end of the (partial) drain phase, water continues to be expelled from the
machine because the drain tube is incorrectly positioned. When this occurs, water loaded by the fill solenoid
during the next phase is directly expelled, so the “full contact” on the pressure switch does not close before
its “time out”.
Thus, if alarm
iF0
occurs, it is a good idea to make sure the drain tube is correctly positioned as
shown in the instruction manual.
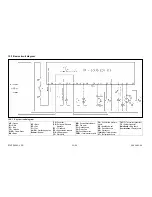
A
B