Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide v11.3
29
Non-Stacking Switches
Non-stacking switches do not have a dedicated switch interconnect. In this case to create an
interconnect between the switches you must utilize one or more ports on each switch to create a Link
Aggregation Group (LAG). This type of Inter-switch connection should utilize link aggregation functions
(if provided by the switch) to aggregate multiple Ethernet ports into a single, logical high bandwidth
interconnect. There are several options depending on the vendor of the switch. Table 15 describes the
most common options
Link Aggregation Type Notes
Static
Static link aggregation defines a set of links that provide a point to
point connection between two switches. These links may or may not
provide failover redundancy or traffic load management.
LACP
Link Aggregation Control Protocol is based on IEEE 802.3ad or IEEE
802.1AX. LACP is a dynamic LAG technology that automatically adjusts
to the appearance or disappearance of links within the defined LACP
group.
PAgP
Cisco’s proprietary Port Aggregation Protocol
Vendor Proprietary
Several switch vendors may provide additional link aggregation options
that are completely proprietary or may be extensions to one of the two
previously mentioned solutions. In most cases, this type of link
aggregation solution is designed to reduce or eliminate the need – and
the overhead – of the Spanning Tree Protocol that must be used in the
two previous options. If available, these proprietary options should be
considered. They may be very useful in allowing the network
administrator to create a more efficient multi-switch layer 2 network
infrastructure for a SAN. Be aware that these proprietary solutions
must support the transmission of IEEE 802.1x flow control and jumbo
frames (if used) to properly support an EqualLogic SAN.
Table 15 Link Aggregation Types
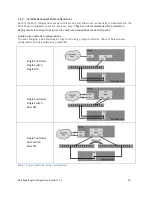
Using a LAG to Connect Stacked Switches
In some situations it may become necessary to expand the EqualLogic SAN by using more than one
single switch stack. For example, you can link multiple stacks by creating a multi-link LACP based LAG
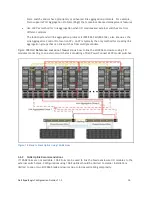
between the switch stacks. A simplified stack plus LAG switch configuration is illustrated in Figure 10.
You should consider the following recommendations when designing this type of SAN:
If possible, use 10Gb connections for all links between each stack.
Distribute the links across multiple switches within each stack (this is known as a ―cross-
stack‖ link aggregation group).
Use LACP or another type of dynamic link aggregation protocol.
Perform tests to determine the best hashing algorithm to use within the link aggregation
group (port channel).
Note:
For best performance and reliability, we recommend that all interconnection paths
between non-stacking switches (LAGs) use a dynamic link aggregation protocol such as LACP.
Содержание EqualLogic PS4000
Страница 1: ...Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide Dell EqualLogic Storage Infrastructure and Solutions ...
Страница 11: ...Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide v11 3 6 Figure 1 Partially Connected Controller Failover ...
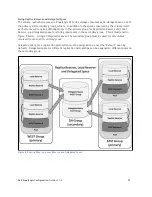
Страница 26: ...Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide v11 3 21 Figure 5 Replication Partnerships with Multiple Groups ...
Страница 44: ...Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide v11 3 39 Figure 14 Mixed Speed Redundant SAN ...
Страница 51: ...Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide v11 3 46 Figure 19 Stack to Stack Uplink Using 1 GbE Links ...