Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide v11.3
26
Port density requirements to support fully redundant configurations and maximum SAN
throughput are as follows:
o
PS4000 family
: 2x 1GbE ports per controller = 4x 1GbE ports total
o
PS5x00 family
: 3x 1GbE ports per controller = 6x 1GbE ports total
o
PS6x00 family
: 4x 1GbE ports per controller = 8x 1GbE ports total
o
PS6x10 family
: 2x 10GbE ports per controller = 4x 10GbE ports total
At least two iSCSI SAN ports per host are required for fully redundant SAN connectivity. Host
ports can be 1GbE or 10GbE.
Quality of Service (QoS) based on what is traditionally designated as IEEE 802.1p is not
currently supported for use with EqualLogic SANs. QoS and Class of Service designations must
be disabled.
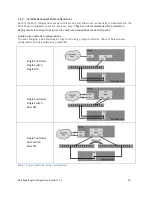
All switches within the SAN must be interconnected such that there is always a path from any
Ethernet port on one array to all other Ethernet ports on all other arrays in the group.
All switches and host network controllers within the infrastructure must have flow control
enabled for optimal performance.
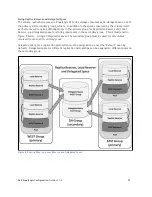
Any EqualLogic SAN group that is required to send or receive replication traffic to/from
another SAN group must have an uninterrupted communications path (ie. ―visibility‖) between
each group.
For EqualLogic PS Arrays, the following general SAN design
recommendations
apply:
Take advantage of your switch’s VLAN capabilities. You should create a VLAN dedicated to iSCSI
traffic (even on dedicated switches). If necessary, create a second VLAN for management
traffic. The actual VLAN configuration of your iSCSI SAN will be dictated by your SAN network
design requirements and the features of the iSCSI SAN switches being used.
Jumbo frames should be enabled. If you choose to use jumbo frames then all nodes in the SAN
fabric must have jumbo frames enabled.
For best performance and reliability, we recommend that all interconnection paths between
non-stacking switches (LAGs) use a dynamic link aggregation protocol such as LACP
4.2.1
Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of service is described as either of the following:
The ability to provide different priority levels to different applications, users, or data flows, or
to guarantee a certain level of performance to a data flow.
A network function implemented in some routers and switches that provides high priority for
certain types of latency-sensitive traffic (for example, VoIP) and lower priority for other types
of traffic (for example, web or http).
PS Series arrays are designed to provide I/O as fast as your network can support it. Therefore, using
QoS with iSCSI traffic does not produce expected or desirable results on the SAN. Also, QoS rules can
affect how well–or even whether–replication succeeds between PS Series groups. If you plan to use QoS,
Dell recommends that you use it only on VLANs that do not carry iSCSI traffic, or on WANs, where
bandwidth is shared with other applications and the PS Series array uses it for time-insensitive
replication traffic.
Dell recommends against using QoS on the SAN.
Содержание EqualLogic PS4000
Страница 1: ...Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide Dell EqualLogic Storage Infrastructure and Solutions ...
Страница 11: ...Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide v11 3 6 Figure 1 Partially Connected Controller Failover ...
Страница 26: ...Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide v11 3 21 Figure 5 Replication Partnerships with Multiple Groups ...
Страница 44: ...Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide v11 3 39 Figure 14 Mixed Speed Redundant SAN ...
Страница 51: ...Dell EqualLogic Configuration Guide v11 3 46 Figure 19 Stack to Stack Uplink Using 1 GbE Links ...