Viper User
Manual (001-5008-000 Rev6)
Page
74
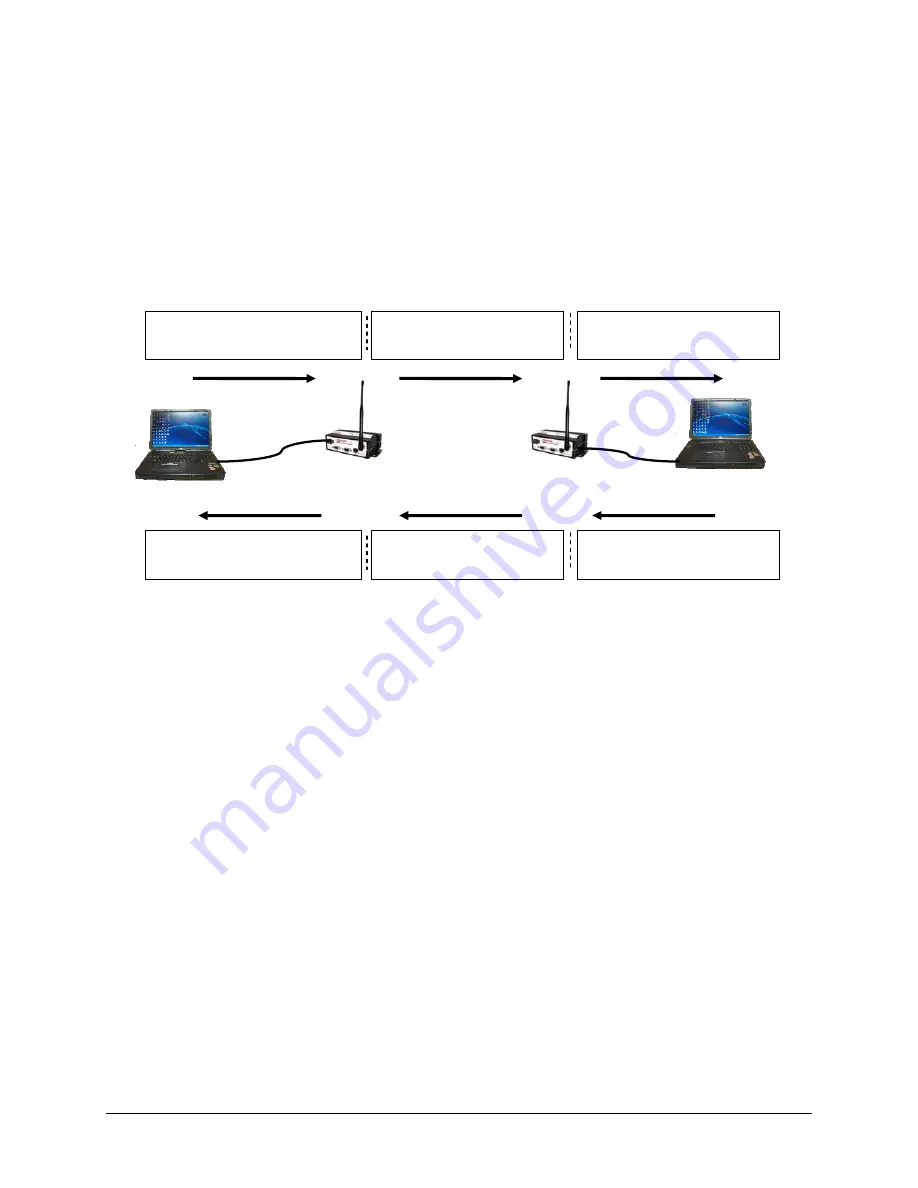
In the example below (Figure 7.22) the following events occur in this order:
1)
Host A sends TCP data packet to Viper A.
2)
Viper A transmits packet over the air to Viper B.
3)
Viper B immediately responds with an RF acknowledgment and sends the TCP data
packet to Host B.
4)
Viper A hears an RF acknowledgement from Viper B and generates a TCP ACK to
send to Host A. Host B receives the original TCP data packet and generates a TCP
ACK to send back over the network.
5)
Viper B receives the TCP ACK but does not send it over the air saving bandwidth on
the Airlink
Figure 7.22 TCP Proxy Example
(1) TCP Packet over Ethernet
(2) TCP Packet over Airlink
(3) TCP Packet over Ethernet
Host A
Host B
Viper A
TCP Proxy Enabled
Viper B
TCP Proxy Enabled
(4) When Viper A hears RF ACK it
generates a TCP ACK and sends it
to Host A
(3) RF ACK over Airlink
(5) TCP ACK is not transmitted
(4) Host B generates TCP ACK.






























