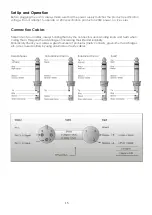
9
1. Mic
Electronically balanced XLR-type inputs for connecting low-impedance
microphones. The input provides extremely low noise and low hum signal
processing. When connecting a microphone make sure that the pin assignment is
correct. Always make sure to read the manual of the microphone you want to
connect. The XLR-inputs are not suitable for connecting line level signals like an
additional mixing console, FX-unit, etc. You have to use the LINE-inputs, when
connecting this kind of equipment.
2. Line
Electronically balanced inputs for connecting a keyboard, CD player, mixer, etc.
You can connect balanced or unbalanced signal sources to the Line input. Do not
connect signal devices to a channel’s MIC and LINE input at the same time. This
will cause mutual interference, which results in level reduction.
Note: When connecting signal sources, please make sure that the corresponding
channel faders and the master faders are at their minimum settings. Otherwise
plug-in noise can occur.
4. Gain
Mic Channel input level is determined by the Gain control. With the Gain control
you can adjust the MIC or LINE input-sensitivity, while optimally matching the
incoming signals to the mixer’s internal operation level. The high gain of this mixer is
ideal when dealing with very low input levels (i.e. vocal recordings or distant sound
sources).
How to set the Input level:
1)
Set the gain control and the corresponding channel fader to their minimum
setting.
2)
Connect the desired sound source (CD player, microphone, etc.) to the
corresponding mic or line input.
3)
Play the sound source at its highest volume setting; respectively, sing or speak as
loud as possible directly into the microphone.
4)
While doing so, adjust the input level using the gain control, so that during the
loudest passages the peak LED is just not lit.
This basic channel setting leaves you at least 8dB headroom. This means, you have
at least 8dB before signal clipping. If you want to make further adjustments to the
channel’s EQ setting, you should repeat step
3
and
4
again.
7. Low cut switch
If you push the “Low Cut” button, a filter will be inserted into the audio chain of the
Sessionmix 12 DSP that has a characteristic 62Hz, 18dB/oct high pass characteristic
to cut any undesired low frequencies. This function can be used to cut the
humming sound or to prevent resonances of low frequencies, when the speakers
are placed in close distance.
8 / 10 / 13. Equalizer SECTION (HI / MID / LOW)
The mixer’s Equalizer section allows shaping of the incoming audio signal. All mono
input channels are fitted with 3-band EQ. The upper (8) and lower (13) shelving
controls have their frequencies fixed at 12 KHz and 80 Hz respectively. The Mid
range control (10) has a peaking response frequency at 2.5 KHz. All 3 bands have
up to 15 dB cut and boost, with a centre detent for. Turning the Equalizer to
Fig. 8
the right amplifies the frequency range, turning to the left attenuates the signal.
Minor changes to the Equalizer control usually produce the best results. Try to avoid
excessive enhancement of the MID band.
11. Parametric Mid
This Control is for adjusting the filter frequency (100 Hz–8kHz) for the equalizer in the
midrange
Содержание Sessionmix 12 DSP
Страница 1: ...Sessionmix 12 DSP ORDERCODE D2193...
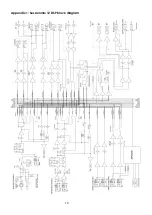
Страница 20: ...18 Appendix 1 Sessionmix 12 DSP block diagram...
Страница 21: ...2008 DapAudio...