DG-104SH VoIP Station Gateway
6
Web-Based Management
Introduction
The DG-104SH VoIP gateway offers an embedded Web-based (hypertext) interface allowing users to manage the
device from anywhere on the network through a standard browser such as Netscape Navigator/Communicator, 4.x
or later, or Microsoft Internet Explorer, 4.x or later. The Web browser acts as a universal access tool and can
communicate directly with the device using HTTP protocol. Your browser screen may vary with the screen shots
(pictures) in this guide.
Note:
This Web-based Management Module does not accept Chinese language input (or other languages
requiring two bytes per character).
Getting Started
The first step in getting started in using Web-based management for your device is to secure a browser. A Web
browser is a program that allows a person to read hypertext, for example, Netscape Navigator, 4.x or later, or
Microsoft Internet Explorer, 4.x or later. Follow the installation instructions for the browser.
The second and last step is to configure the IP interface of the device. This can be done manually through a console.
See the
Configuring the
VoIP Gateway using a Web Browser
section of the “
Configuration
” chapter for specific
instructions.
Management
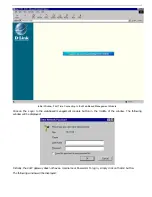
To begin managing your device simply run the browser you have installed on your computer and point it to the IP
address you have defined for the device. The URL in the address bar should read something like:
http://123.123.123.123, where the numbers 123 represent the IP address of the device.
In the page that opens, click on the following
Login to the web-based management module
button:
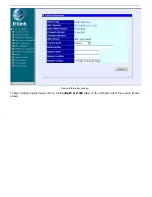
This categories listed on the left-side of the web-based management module include:
Config IP & H.323
(
Config
Device IP Address
and
Config H.323
),
Device Information
,
Telephony Configuration
(
System Gains
and
Prefer Codec Table
),
Dial Address Configuration
(
Basic
and
Advance
),
DHCP Configuration
(
Dynamic
IP Assignment
and
Static IP Assignment
),
NAT Configuration
(
NAT Configuration
and
Local Server
Configuration
),
SNMP Trap Configuration
,
Administration Management
,
Monitor
(
Ethernet
Statistics, DSP Statistics
,
Tcid Configuration
, and
Coding Profile
),
Firmware and Configuration
Update
,
Save Changes
,
Factory Reset
, and
Restart System
.