Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
31
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Smart Switch with Resilient Clustering Technology and PoE
Setting Timer
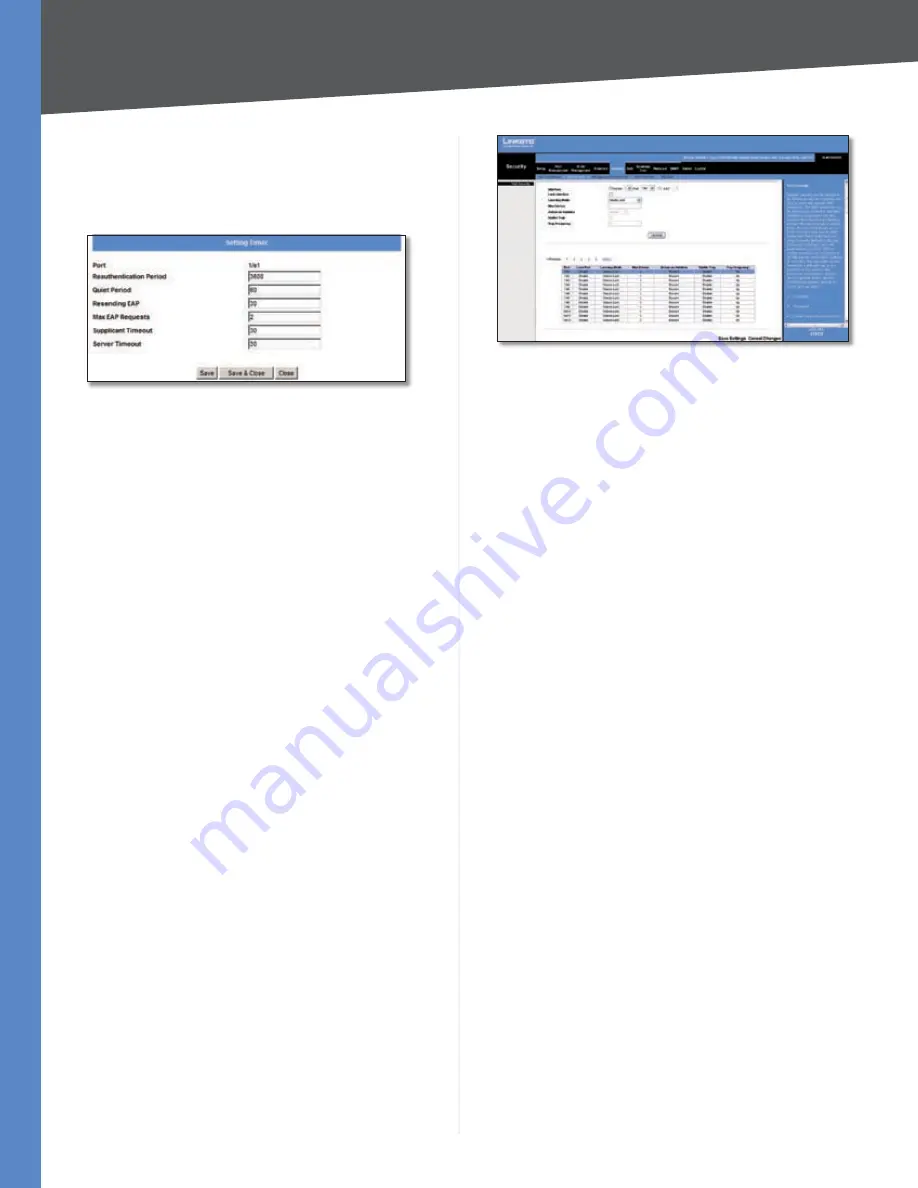
The
Setting Timer
screen appears when you click
Setting
Timer
on the
802.1x Settings
screen. You use the
Setting
Timer
screen to configure a port’s 802.1x functionality.
Security > 802.1x Settings > Setting Timer
Port
Displays the port name.
Reauthentication Period
Specifies
the
number
of seconds after which a connected client must be
reauthenticated. The range is
300
to
4246725
seconds. The default value is
3600
seconds.
Quiet Period
Specifies the time that a switch port waits
after
Max EAP Requests
is exceeded before attempting
to acquire a new client. The range is
1
to
65535
seconds.
The default is
60
seconds.
Resending EAP
Specifies the time that the switch waits
for a response to an EAP request/identity frame from the
client before retransmitting an EAP packet. The range is
1
to
65535
seconds. The default is
30
seconds.
Max EAP Requests
Specifies the maximum number
of times the switch port will retransmit an EAP request
packet to the client before it times out the authentication
session. The range is
1
to
10
times. The default is
2
retries.
Supplicant Timeout
Displays the number of seconds that
lapses before EAP requests are resent to the supplicant. The
range is
1
to
65535
seconds. The default is
30
seconds.
Server Timeout
The number of seconds that lapses
before the switch resends a request to the authentication
server The range is
1
to
65535
. The default is
30
seconds.
Click
Save
to save your changes and leave the screen
open. Click
Save & Close
to save your changes and close
the screen. Click
Close
to close the screen without saving
your changes.
Security > Port Security
The
Port Security
screen is used to configure a port’s
security settings.
Network security can be increased by limiting access on
a specific port only to users with specific MAC addresses.
MAC addresses can be dynamically learned or statically
configured.
Security > Port Security
Locked port security monitors both received and learned
packets that are received on specific ports. Access to the
locked port is limited to users with specific MAC addresses.
These addresses are either manually defined on the port,
or learned on that port up to the point when it is locked.
When a packet is received on a locked port, and the
packet’s source MAC address is not tied to that port (either
it was learned on a different port, or it is unknown to the
system), the protection mechanism is invoked, and can
provide various options. Unauthorized packets arriving at
a locked port are either:
Forwarded
Discarded
Cause the port to be shut down
Locked port security also enables storing a list of MAC
addresses in the configuration file. The MAC address list
can be restored after the device has been reset.
Disabled ports can be reactivated from the
Port Settings
screen of the Port Management tab.
Interface
Select
Unit No.
or
LAG
, then select the desired
interface from the appropriate drop-down menu.
Lock Interface
Select this option to lock the interface.
The default is not selected (interface not locked).
Learning Mode
Defines the locked port type. This field
is enabled only if
Lock Interface
is not selected. The
possible values are:
Classic Lock
Locks the port using the classic lock
mechanism. The port is immediately locked, regardless
of how many addresses have already been learned.
Limited Dynamic Lock
Locks the port by deleting
the current dynamic MAC addresses associated with
the port. The port learns up to the maximum number
of addresses allowed on the port. Both relearning and
aging MAC addresses are enabled.
In order to change the
Learning Mode
, the
Lock Interface
must be unselected. Once the
Learning Mode
is changed,
the
Lock Interface
can be reinstated.
•
•
•
•
•






























