Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
24
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Smart Switch with Resilient Clustering Technology and PoE
Port
The port whose PoE settings are being configured.
To configure a different port, select it from the drop-down
menu.
Admin Status/Enable
This indicates if PoE is enabled or
disabled on the port. To enable PoE on the port, keep the
default,
Enable
(option selected). To disable PoE on the
port, unselect the
Enable
option.
Priority
This indicates the PoE port’s priority. The values
are Critical, High, and
Low
(default).
Power Allocation
(Read-only) This indicates the actual
amount of power in milliwatts that the switch can supply
on the port.
Power Consumption
(Read-only) This indicates the
amount of power that is currently being consumed on the
port.
Click
Save Settings
to save your changes. Click
Cancel
Changes
to cancel your changes.
VLAN Management
A VLAN is a group of ports that can be located anywhere
in the network, but communicate as though they belong
to the same physical segment.
VLANs help to simplify network management by allowing
you to move devices to a new VLAN without having to change
any physical connections. VLANs can be easily organized to
reflect departmental groups (such as Marketing or R&D),
usage groups (such as e-mail), or multicast groups (used
for multimedia applications such as videoconferencing).
You can create up to 128 VLANs on the Switch.
VLAN Management > Create VLAN
The
Create VLAN
screen lets you create and configure
global parameters for VLANs.
VLAN Management > Create VLAN
Single VLAN
To create a single VLAN, enter the VLAN ID and VLAN
Name, up to 32 characters long, and click
Add
.
VLAN ID
ID of the VLAN being configured (
2
-
403
, no
leading zeroes).
VLAN Name
Name of the VLAN (1 to 32 characters).
VLAN Range
To create a range of VLANs, enter the range of their IDs in
the
VLAN Range
fields and then click
Add Range
.
VLAN Table
This lists the ID, name, and status of each configured VLAN,
and the total number of VLANs. The VLAN status is either
Static
(user-defined VLAN) or
Default
(default VLAN).
To remove a VLAN or a range of VLANs, select the VLANs in
the VLAN Table, then click
Delete
.
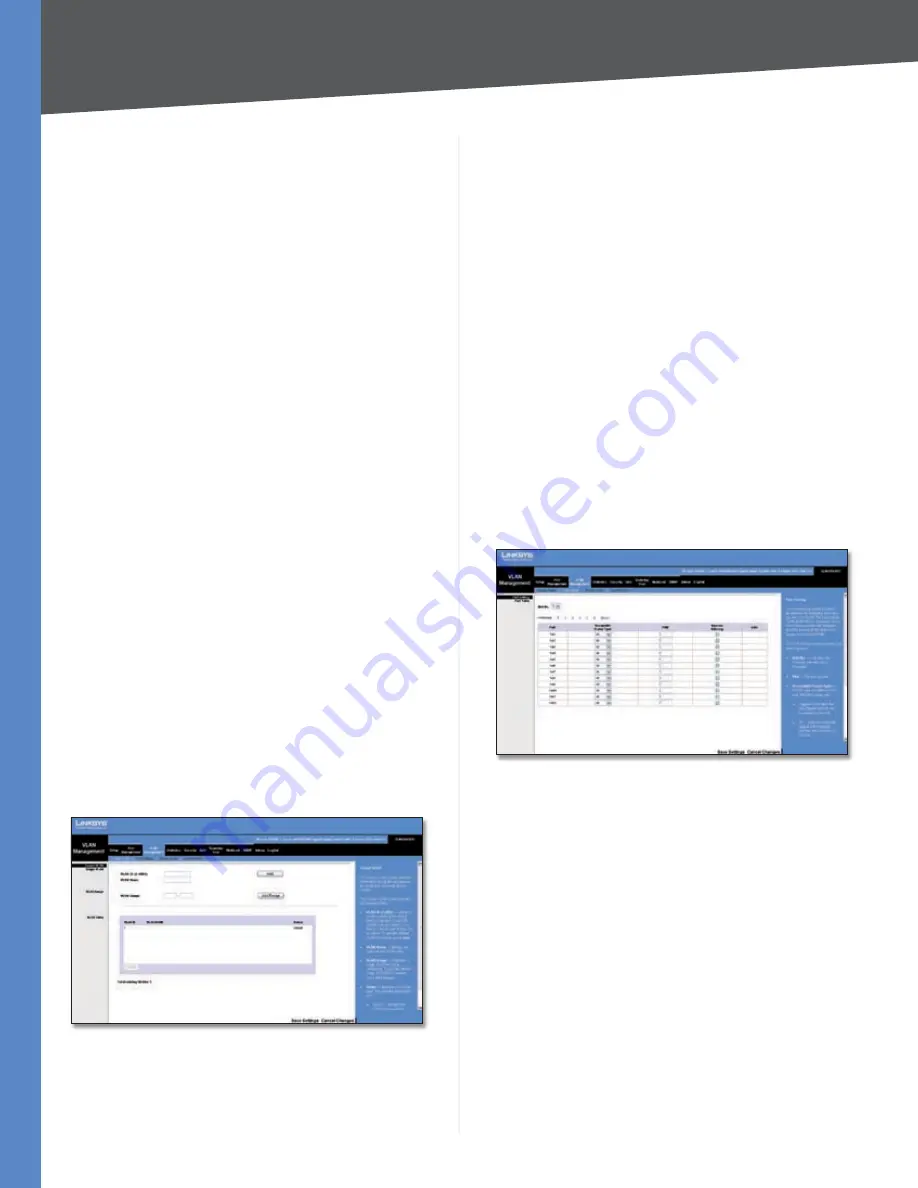
VLAN Management > Port Setting
The
Port Setting
screen allows you to manage the ports in
a VLAN. The port default VLAN ID (PVID) is configured from
the
Port Setting
screen. All untagged packets arriving at a
VLAN port are tagged with the port’s PVID.
VLAN Management > Port Setting
You can configure VLAN behavior for specific ports,
including the accepted frame type, VLAN identifier (PVID),
and ingress filtering.
Unit No.
The number of the unit that you are managing.
Port
The number of the port.
Acceptable Frame Type
This specifies the type of frames
that the port will accept. If
All
(default) is selected, the port
will accept all frame types, including tagged or untagged
frames. If
Tagged
is selected, the port accepts only tagged
frames. When set to
All
, each untagged frame received is
assigned to the specific VLAN that matches the PVID.
PVID
Use this field to select the VLAN ID that will be
assigned to untagged frames received on the port.
Valid IDs are
1
(default) to
403
. VLAN 4094 is reserved
for internal use. VLAN 4095 is defined per standard and
industry practice as the Discard VLAN. Frames tagged for
the Discard VLAN are dropped.






























