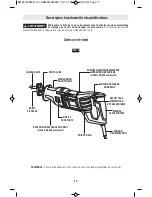
-10-
- For ferrous metals, iron and steel, use
machine or cutting oil along the surface
to be cut.
5. When cutting thin metal, "sandwich" the
material between two pieces of scrap wood.
Clamp or put in a bench vise. One piece of
lumber on top of the metal can be used with
adequate clamping. Place your cut lines or
design on the wood.
6. Don’t force the cutting. Let the saw and
blade do the work.
When operating the saw
continuously
and
for
prolonged periods of time, the gearbox may
become hot to the touch. To reduce the risk of
injury, wear gloves during saw operation.
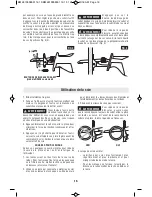
POCKET CUTS
POCKET/PLUNGE CUTS
The reciprocating saw can be used to make
plunge cuts into softer material, (for example,
wood or light building materials for walls),
without a starting hole (Fig. 5).
1. Mark the line to be cut clearly on the work.
2. Set the tool with one edge of the footplate
firmly against the material.
3. Place the tip of the blade (not running) on the
line to be cut.
4. Tilt the saw so that the blade clears the work.
5. Squeeze the trigger switch and carefully
engage the moving saw blade into the material.
6. After the blade penetrates through the work,
continue sawing along the marked outline.
NOTES:
To make plunge cutting easier, use a heavy
gauge blade, install the blade with the teeth
facing upward, and hold the saw upside down
as shown (Fig. 6).
Do not plunge cut in metal surfaces.
In thick materials and in harder materials,
such as metal, plunge cutting should not be
attempted. Such materials can be cut with the
recip saw only by starting the cut from the
edge of the material or from a hole drilled all
the way through the material that is large
enough to fit the saw blade.
The use of any accessories
not specified in this manual
may create a hazard.
!
WARNING
FIG. 5
FIG. 6
!
WARNING
BM 2610009031 12-10:BM 2610009031 12-10 12/17/10 10:18 AM Page 10