■
Chapter 3 Battery Power & Power Management
Using Windows Power Options
Windows Power Management provides basic power saving features. In the Windows Power Options
Properties [Start > Settings > Control Panel > Performance and Maintenance > Power Options] dialogue
box, you may enter time-out values for display and hard disk drive. Windows power manager saves
power by turning off the hard drive after 1 minute of inactivity, for example.
Windows’ Power Schemes
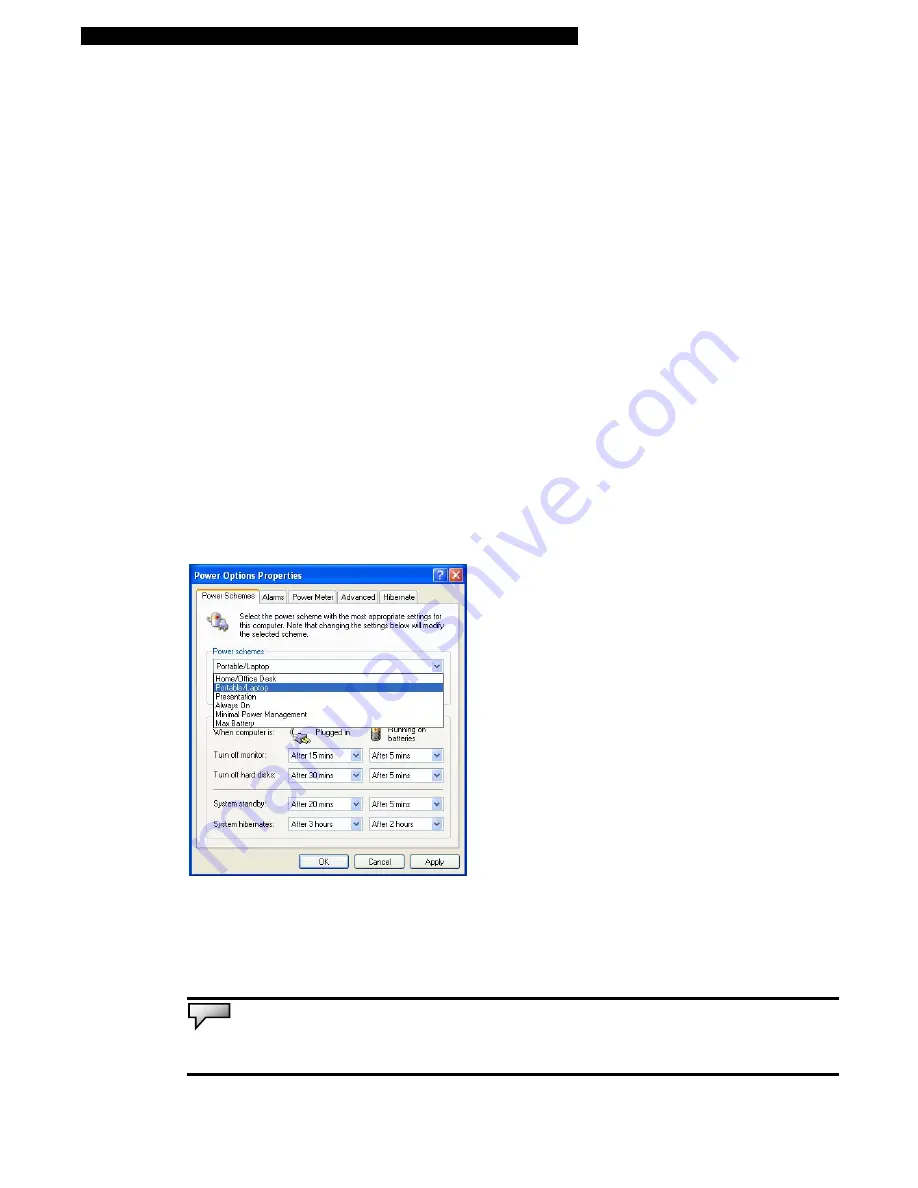
The power management control panel in Windows XP, known as Power Schemes, is designed to
provide the user with an easy-to-use interface. The Power Schemes tab can be found in the Power
Options Properties panel that is accessible via the control panel window.
Schemes are easy to understand, based on notebook usage scenarios, and control not only
processor power usage but other system peripherals as well.
Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel > Performance and Maintenance] and double-click the
Power Options icon.
Always on
mode puts the processor into maximum performance mode, which provides no power
saving. The other schemes control processor performance based on demand. For example, Max
Battery mode lowers the processor’s speed and voltage to conserve power as much as possible.
In this dialog box, you can manually set the LCD and hard drive’s time-out values in the “Plugged
in” column and in the “Running on batteries” column. Lower time-out values will conserve battery
power.
Note:
Also consult Windows user guide for more information on how to use Windows power management functions.
Note:
Actual dialogue box shown above may appear slightly different.






























