27
8126F–AVR–05/12
ATtiny13A
6.3.1
Switching Time
When switching between prescaler settings, the System Clock Prescaler ensures that no
glitches occur in the clock system and that no intermediate frequency is higher than neither the
clock frequency corresponding to the previous setting, nor the clock frequency corresponding to
the new setting.
The ripple counter that implements the prescaler runs at the frequency of the undivided clock,
which may be faster than the CPU’s clock frequency. Hence, it is not possible to determine the
state of the prescaler – even if it were readable, and the exact time it takes to switch from one
clock division to another cannot be exactly predicted.
From the time the CLKPS values are written, it takes between T1 + T2 and T1 + 2*T2 before the
new clock frequency is active. In this interval, 2 active clock edges are produced. Here, T1 is the
previous clock period, and T2 is the period corresponding to the new prescaler setting.
6.4
Register Description
6.4.1
OSCCAL – Oscillator Calibration Register
• Bit 7 – Res: Reserved Bit
This bit is reserved bit in ATtiny13A and it will always read zero.
• Bits 6:0 – CAL[6:0]: Oscillator Calibration Value
Writing the calibration byte to this address will trim the internal Oscillator to remove process vari-
ations from the Oscillator frequency. This is done automatically during Chip Reset. When
OSCCAL is zero, the lowest available frequency is chosen. Writing non-zero values to this regis-
ter will increase the frequency of the internal Oscillator. Writing 0x7F to the register gives the
highest available frequency.
The calibrated Oscillator is used to time EEPROM and Flash access. If EEPROM or Flash is
written, do not calibrate to more than 10% above the nominal frequency. Otherwise, the
EEPROM or Flash write may fail. Note that the Oscillator is intended for calibration to 9.6 MHz or
4.8 MHz. Tuning to other values is not guaranteed, as indicated in
To ensure stable operation of the MCU the calibration value should be changed in small steps. A
variation in frequency of more than 2% from one cycle to the next can lead to unpredicatble
behavior. Changes in OSCCAL should not exceed 0x20 for each calibration. It is required to
ensure that the MCU is kept in Reset during such changes in the clock frequency
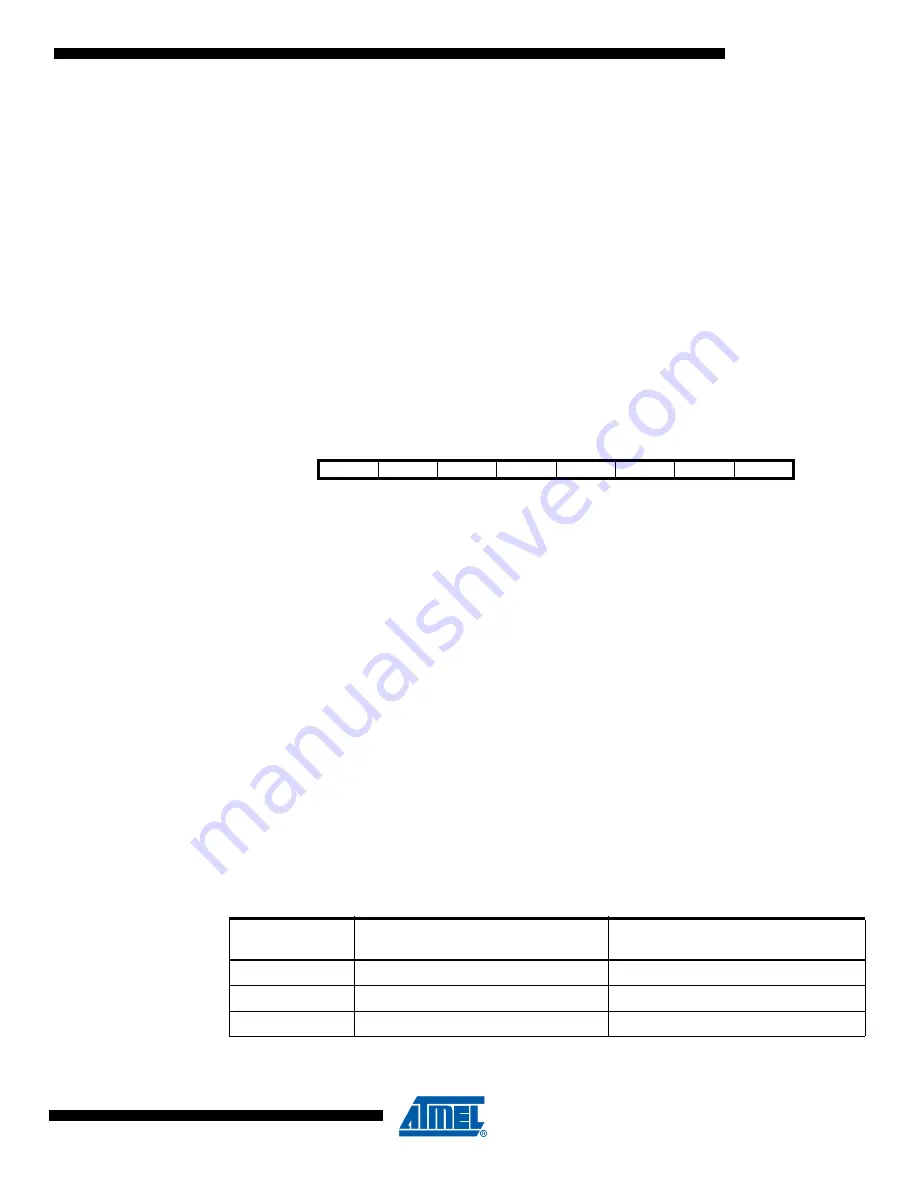
Bit
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
–
CAL6
CAL5
CAL4
CAL3
CAL2
CAL1
CAL0
OSCCAL
Read/Write
R
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
Initial Value
0
Device Specific Calibration Value
Table 6-7.
Internal RC Oscillator Frequency Range
OSCCAL Value
Typical Lowest Frequency
with Respect to Nominal Frequency
Typical Highest Frequency
with Respect to Nominal Frequency
0x00
50%
100%
0x3F
75%
150%
0x7F
100%
200%
















































