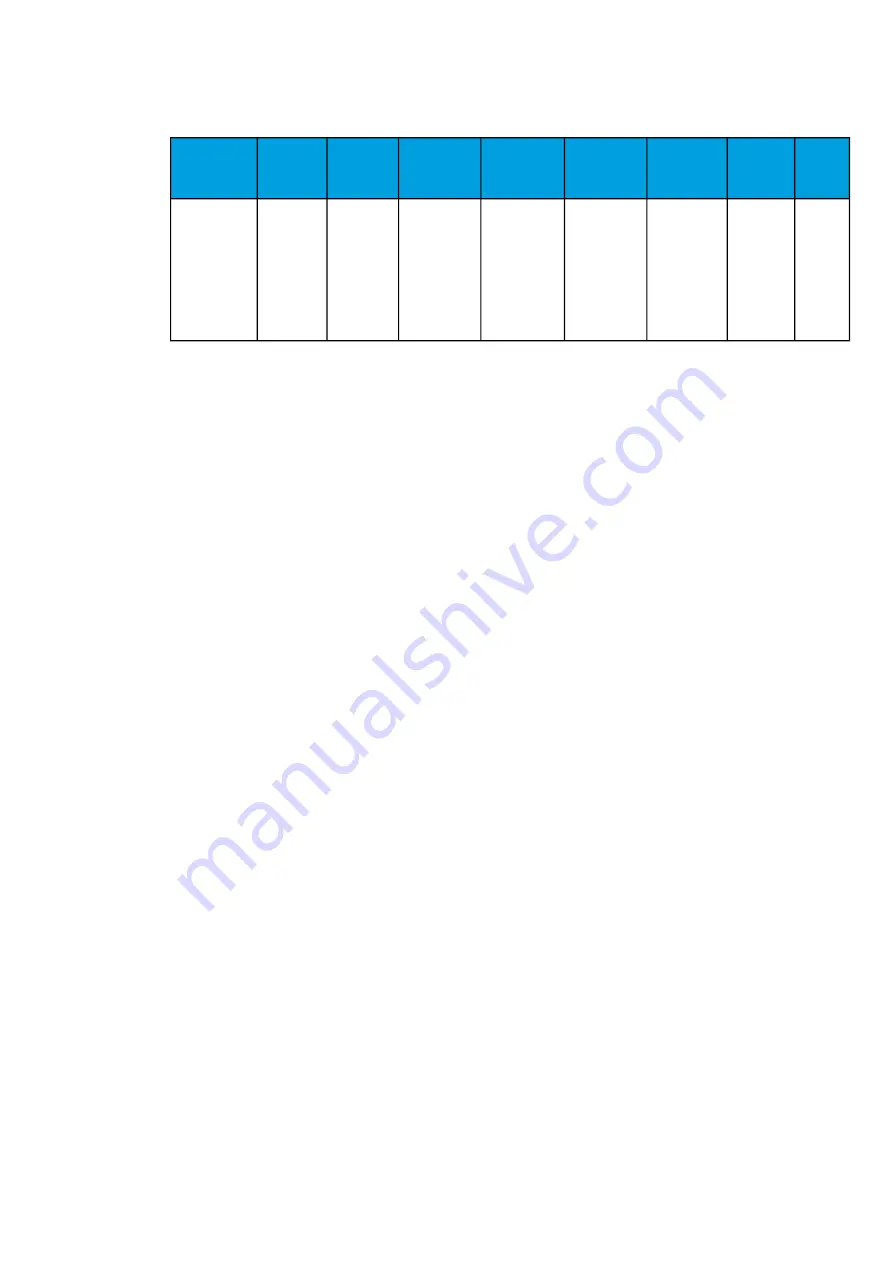
Table. 5.3.6 - 85. Register content.
Date and
time
Event
code
Trip time
remaining
Started
FWD
Spikes
FWD
Started
REV
Spikes
REV
Spikes to
trip
Setting
group
in use
dd.mm.yyyy
hh:mm:ss.mss
7296-7307
Descr.
Time
remaining
from the
set
operating
time.
YES/
NO indication
of the
forward start
in this fault.
The
calculated
cumulative
amount of
forward
(faulty)
feeder spikes.
YES/
NO indication
of the
reverse start
in this fault.
The
calculated
cumulative
amount of
reverse
(healthy)
feeder spikes
Set spikes
to trip
subtracted
by the
cumulative
forward
spikes. If 0
spikes, it
trips.
1...8
5.3.7 Negative sequence overcurrent/ phase current reversal/ current unbalance
protection (I2>; 46/46R/46L)
The current unbalance function is used for instant and time-delayed unbalanced network protection
and for detecting broken conductors. The number of stages in the function depends on the
relay model. The operating decisions are based on negative and positive sequence current magnitudes
which the function constantly measures. In the broken conductor mode (I2/I1) the minimum allowed
loading current is also monitored in the phase current magnitudes.
There are two possible operating modes available: the I2 mode monitors the negative sequence
current, while the I2/I1 mode monitors the ratio between the negative sequence current and the
positive sequence current. The relay calculates the symmetrical component magnitudes in use from
the phase current inputs
I
L1
,
I
L2
and
I
L3
. The zero sequence current is also recorded into the registers
as well as the angles of the positive, negative and zero sequence currents in order to better verify any
fault cases. The blocking signal and the setting group selection control the operating characteristics of
the function during normal operation, i.e. the user or user-defined logic can change function
parameters while the function is running.
The outputs of the function are the START, TRIP and BLOCKED signals. The current unbalance
function uses a total of eight (8) separate setting groups which can be selected from one common
source.
The function can operate on instant or time-delayed mode. In time-delayed mode the operation can be
selected between definite time (DT) or inverse definite minimum time (IDMT). The IDMT operation
supports both IEC and ANSI standard time delays as well as custom parameters.
The operational logic consists of the following:
• input magnitude selelction
• input magnitude processing
• threshold comparator
• block signal check
• time delay characteristics
• output processing.
The inputs for the function are the following:
• operating mode selections
• setting parameters
• digital inputs and logic signals
• measured and pre-processed current magnitudes.
A
AQ
Q-F215
-F215
Instruction manual
Version: 2.04
142
Содержание AQ-F215
Страница 1: ...AQ F215 Feeder protection IED Instruction manual ...
Страница 430: ...Figure 7 4 261 Example block scheme A AQ Q F215 F215 Instruction manual Version 2 04 429 ...
Страница 452: ...Figure 8 14 284 Panel cutout dimensions and device spacing A AQ Q F215 F215 Instruction manual Version 2 04 451 ...
Страница 487: ...10 Ordering information A AQ Q F215 F215 Instruction manual Version 2 04 486 ...






























