Voice over WLAN Mobile IP Touch Design Guide R2.0
3.8. Predictive Environment Solution Options (Responding to RFx)
When answering an RFP or RFI, normally, there is little possibility of scheduling a Site Survey for various
reasons: Building under construction or not yet built, short delay to answer the RFP, fair competition
clause, etc. In these cases we can make a compromise between absolute accuracy of design and ease of
offer presentation by trying to evaluate the user environment and theorize the required quantity of
Access Points. It is essential to never forget to clearly indicate on the RFP, or unsolicited bid, that a
compulsory Site Survey is required to verify the correct quantity of AP and their related locations.
3.8.1. Manual Calculation of Predictive Coverage
The following predictive method can be used to produce a budgetary design. Many environment
variables like wave propagation, type of building, wall structure, interferences, etc. may, unexpectedly-
affect the size quality, and complexity of the RF (Radio Frequency) coverage plan.
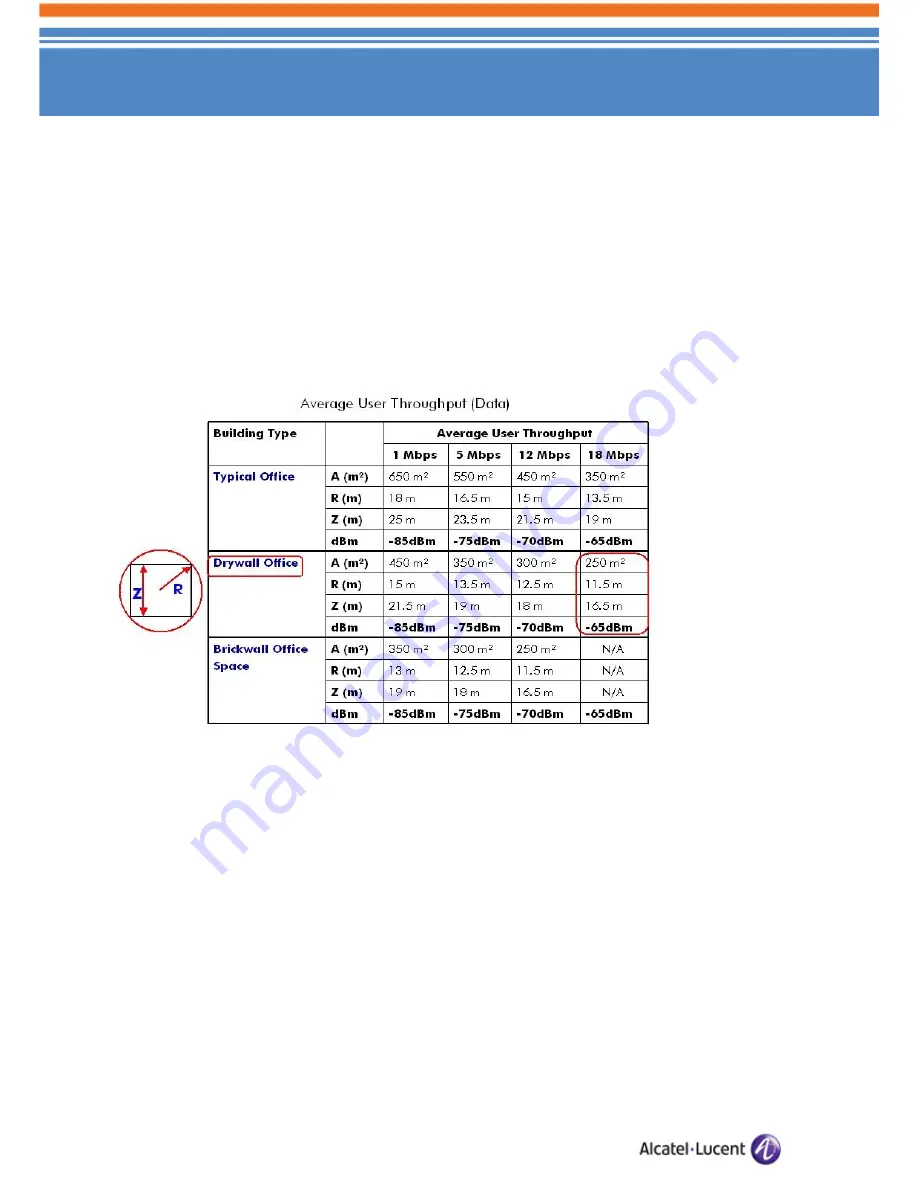
Figure 18: User Throughput (type of Wall) for 802.11g
In the above chart:
R=”The coverage radius provided by an AP and is used to define a perimeter or radial-footprint.”
Z=”The coverage square contained within the perimeter(R).”
A=”The area of (Z
2
) covered in square meters.”
For the following example (Drywall construction office building), use of the above defined calculation
table results in an estimated bandwidth average of roughly 18 Mbps for data 802.11g Wi-Fi traffic. We
can apply the same calculation strategy to VoWLAN simply by focusing on the performance of 802.11b at
an estimated signal strength of -65dBm (target limit for voice.)
ESD/ Central Pre Sales / DF/ PH
37/45
January 2007 – Ed 01









































