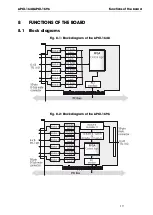
Glossary
APCI-1648/APCI-1696
24
11
GLOSSARY
Table 11-1: Glossary
Term
Description
A/D converter
=
ADC
An electronic device that produces a digital output directly
proportional to an analog signal output.
Acquisition
The process by which data is gathered by the computer for
analysis or storage.
Bus
The group of conductors that interconnect individual circuitry
in a computer. Typically, a bus is the expansion vehicle to
which I/O or other devices are connected. Examples of PC
buses are PCI, PC Card (PCMCIA), ISA (AT), and EISA bus.
Counter
A circuit that counts pulses or measures pulse duration
D/A converter
=
DAC
A device that converts digital information into a corresponding
analog voltage or current.
Data acquisition
Gathering information from sources such as sensors and
transducers in an accurate, timely and organized manner.
Modern systems convert this information to digital data which
can be stored and processed by a computer.
DC voltage
= Direct current voltage
DC voltage means that the voltage is constant respecting the
time. It will always fluctuate slightly. Especially at switching
on and switching off the transition behaviour is of high
significance.
Digital signal
A signal which has distinct states. Digital computers process
data as binary information having either 1 or 0 states.
Disturb signal
Interferences that occur during the transfer caused by reduced
bandwidth, attenuation, gain, noise, delay time etc.
Driver
A part of the software that is used to control a specific
hardware device such as a data acquisition board or a printer.
Gain
The factor by which an incoming signal is multiplied.
Ground
A common reference point for an electrical system.
Inductive loads
The voltage over the inductor is U=L.(dI/dt), whereas L is the
inductivity and I is the current. If the current is switched on
fast, the voltage over the load can become very highly for a
short time.
Interrupt
A signal to the CPU indicating that the board detected the
occurrence of a specified condition or event.
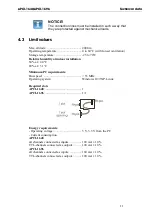
Limit value
Exceeding the limit values, even for just a short time, can lead
to the destruction or to a loss of functionality.
Noise immunity
Noise immunity is the ability of a device to work during an
electromagnetic interference without reduced functions.
Operating voltage
The operating voltage is the voltage that occurs during the
continuous operation of the device. It may not exceed the
continuous limit voltage. Furthermore, any negative operation
situations, such as net overvoltages over one minute at
switching on the device must be taken in consideration.