XVME-6300
6U VME Intel i7 Core Processor Board
Acromag, Inc. Tel: 248-295-0310
- 28 -
www.acromag.com
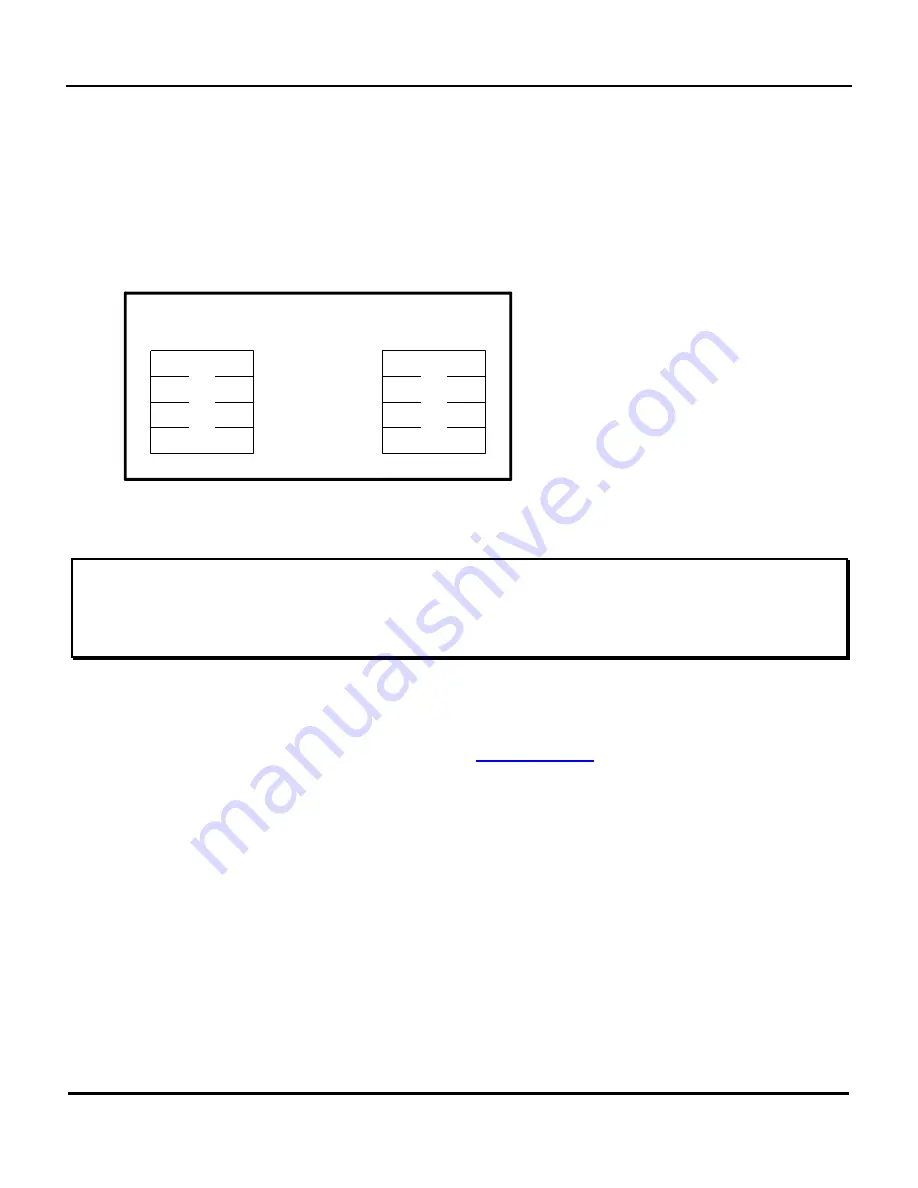
Byte-Ordering Schemes
The Motorola family of processors stores data with the least significant byte located at the highest address
and the most significant byte at the lowest address. This is referred to as a big-endian bus and is the
VMEbus standard. The Intel® family of processors stores data in the opposite way, with the least significant
byte located at the lowest address and the most significant byte located at the highest address. This is
referred to as a little-endian (or PCI) bus. This fundamental difference is illustrated in Figure 3-1, which
shows a 32-bit quantity stored by both architectures, starting at address M.
Fig. 0-1 shows byte ordering schemes
Note
The two architectures differ only in the way in which they store data into memory, not in the way in which they
place data on the shared data bus.
The XVME-6300 contains a TSI-148 chip that performs address-invariant translation between the PCIbus
(Intel® architecture) and the VMEbus (Motorola architecture) and byte-swapping hardware to reverse the
TSI-148 chip byte-lane swapping. (Contact Tundra at
for a PDF version of the TSI-148
manual.) Figure 4-2 shows address-invariant translation between a PCI bus and a VMEbus.
High Byte
Low Byte
Low Byte
High Byte
INTEL
MOTOROLA
Address
M
M+1
M+2
M+3












































