BusWorks® 961/962EN User’s Manual Modbus TCP/IP Differential I/V Input
___________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Acromag, Inc. Tel:248-624-1541 Fax:248-624-9234 Email:
http://www.acromag.com
21
Checksum
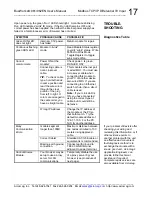
TCP FRAME
MODBUS FRAME
Transaction Identifier
Modbus Frame
Length Field
Protocol Identifier
Data
Address
Function Code
Modbus Checksum
Not Included
TCP/IP is the foundation for the World Wide Web and refers to
Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol. TCP/IP allows blocks
of binary data to be exchanged between computers. The primary function of
TCP is to ensure that all packets of data are received correctly. IP makes
sure that messages are correctly addressed and routed. Note that the
TCP/IP combination does not define what the data means or how the data is
to be interpreted, it is merely a
transport protocol
.
Modbus is an
application protocol
. It defines rules for organizing and
interpreting data and is essentially a messaging structure that is independent
of the underlying physical layer. It is freely available and accessible to
anyone, easy to understand, and widely supported by many manufacturers.
Modbus TCP/IP uses TCP/IP and Ethernet to carry the data of the Modbus
message structure between devices. That is, Modbus TCP/IP combines a
physical network (Ethernet), with a networking standard (TCP/IP), and a
standard method of representing data (Modbus). A Modbus TCP/IP
message is simply a Modbus communication encapsulated in an Ethernet
TCP/IP wrapper.
In practice, Modbus TCP embeds a Modbus data frame into a TCP frame,
without the Modbus checksum, as shown in the following diagram. The
Modbus checksum is not used, as the standard ethernet TCP/IP link layer
checksum methods are instead used to guaranty data integrity.
Note that the Modbus address field is referred to as the
Unit Identifier
in
Modbus TCP. In a typical slave application, the Unit ID is ignored and just
echoed back in the response.
The operation of the 961/962EN industrial Ethernet modules is very similar
to Acromag’s 913/914MB ModBus modules. The operation over Ethernet is
essentially transparent to the Modbus register/command structure. If you
are already familiar with Modbus or with Acromag Series 900MB modules,
then you are already familiar with the operation of the 961/962EN modules.
A host is any device on any network. On TCP/IP networks, each host has
one or more unique IP addresses. This module connected to an ethernet
network is a host.
An IP Address is a unique identification number for any host (this module) on
any TCP/IP network (including the internet). The IP address is made up of
four octets (8 bits), each octet having a value between 0-255 (00H-FFH).
The IP address is comprised of two parts: the network address (first part)
and the host address (last part). The number of octets of the four total that
belong to the network address depend on the Class definition (see below).
ABOUT MODBUS
TCP/IP
You can find more information
on Modbus TCP/IP by visiting
our web site and down-loading
whitepaper 8500-765,
Introduction To Modbus
TCP/IP.
IP Addressing