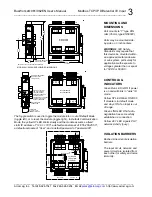
BusWorks® 961/962EN User’s Manual Modbus TCP/IP Differential I/V Input
__________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Acromag, Inc. Tel:248-624-1541 Fax:248-624-9234 Email:
http://www.acromag.com
10
An
IP Address
is a unique identification number for any host (this module)
on any TCP/IP network (including the internet). The IP address is made up
of four octets (8 bits), each octet having a value between 0-255 (00H-FFH).
It is expressed here in decimal form, with a period placed between octets.
A
Static IP Address
is as the name implies—
static
, and represents a unique
fixed IP Address that is generally assigned by your service provider or
system administrator. The default static IP address assigned to this module
from the factory is 128.1.1.100 (refer to product side label).
NOTE:
In order to network your PC with an Acromag module, you may have
to consult with your network administrator and either temporarily change
your TCP/IP configuration (see TCP/IP Properties of Network Configuration
in Windows), or create a separate private network using a second network
adapter installed in your PC (recommended). The necessary steps will vary
with your operating system. Refer to Acromag Application Note 8500-734 to
help accomplish this (located on the CDROM shipped with your module or
via download from our web site at www.acromag.com).
The
Number of Sockets
refers to the number (1-10) of Modbus TCP/IP
access points to allow for this host. The default allows up to 10 sockets, but
you can restrict access by reducing this number. Internally, the module uses
port number 502 which is reserved for Modbus.
The
DNS Server
refers to the IP address of the Domain Name Server used
on this network. A DNS server relates symbolic names to actual IP
addresses, while the DHCP server is responsible for dynamically passing out
IP addresses.
A
Subnet Mask
is used to subdivide the host portion of the IP address into
two or more subnets. The subnet mask will flag the bits of the IP address
that belong to the network address, and the remaining bits correspond to the
host portion of the address. The unique subnet to which an IP address
refers to is recovered by performing a bitwise AND operation between the IP
address and the mask itself, with the result being the sub-network address.
Gateway
refers to the IP Address of the gateway, if your local area network
happens to be isolated by a gateway. Typically, it is assigned the first host
address in the subnet. If a gateway is not present, then this field should
contain an unused address within the host subnet address range.
The
Host Name
is the name to be assigned to this host if its address
happens to be assigned dynamically using DHCP.
The
Active IP Address
refers to the current IP Address being used by this
host, as opposed to any new assignments being made via this page.
The
MAC Address
refers to the Media Access Control Address that
uniquely identifies the hardware of this device. This is a unique fixed
address assigned to this module at the factory. On IEEE 802 networks, the
Data Link Control (DLC) layer of the OSI Reference Model is divided into two
sublayers: the Logical Link Control (LLC) layer, and the Media Access
Control (MAC) layer. The MAC layer interfaces directly with the network
media (each different type of network media requires a different MAC layer).
WEB BROWSER
Network Configuration
Note that Acromag Series
9xxEN Ethernet I/O modules
may take from 3-30 seconds to
boot upon power-up,
depending on your network
configuration and whether a
DHCP server is present.
This module can be placed
into a default communication
mode via the DFT toggle
switch at the front of the
module.
Default Mode uses a static IP
address of “128.1.1.100”, a
default subnet mask of
“255.255.255.0”, a default
username “User”, and a
default password
“password00”.