Operating Instructions
2K2100 with STW
Initial installation
The pulley should be balanced to quality 6.3 as
per VDI Directive 2060 and DIN ISO 1940 Part 1
+ Part 2 in order to ensure low-vibration
operation. Note the axial and radial runout of the
centering device on the belt pulley and belt
grooves in relation to the centering device.
CAUTION
Note the maximum specified tensioning force
when tensioning the belts in order to prevent
bearing overload.
The average belt force must be between the
bearings. When assembling, it must be possible
to easily slide the pulley onto the output flange.
Heat the pulley if necessary.
21
3.6.2
Option: version with coaxial output,
only on request
In the case of the version with coaxial output
(shaft stub), also note the balancing type for the
output (see section 3.2).
3.7
Electrical connection, gearchange
The gearbox is electrically connected using the
supplied 8-pole Harting connector (HAN 8 U).
The plug-in connection is located on the shift unit.
3.7.1
Shift unit
Technical data:
Power consumption
85 W
Supply voltage
24 V DC
±
10%
Current consumption 5 A
(max. pull-in current)
The required cable lead diameter is 1.5 mm².
The 24 VDC supply voltage and 5 A current
consumption must be assured at the shift unit plug
on the gearbox.
Losses due to cable length and transition resistors
must be taken into account.
If switching to the shift unit by relay, we
recommend using a varistor, e.g. Siemens type
S14-30 (30 V) to connect to the 24 V voltage pin
2 and pin 3.
Scope of supply:
Sleeve housing, screw connection, socket insert
and 8 jacks, type Harting AWG16, (ZF order no.
4161 298 004).
The shift unit can only be obtained as a complete
part.
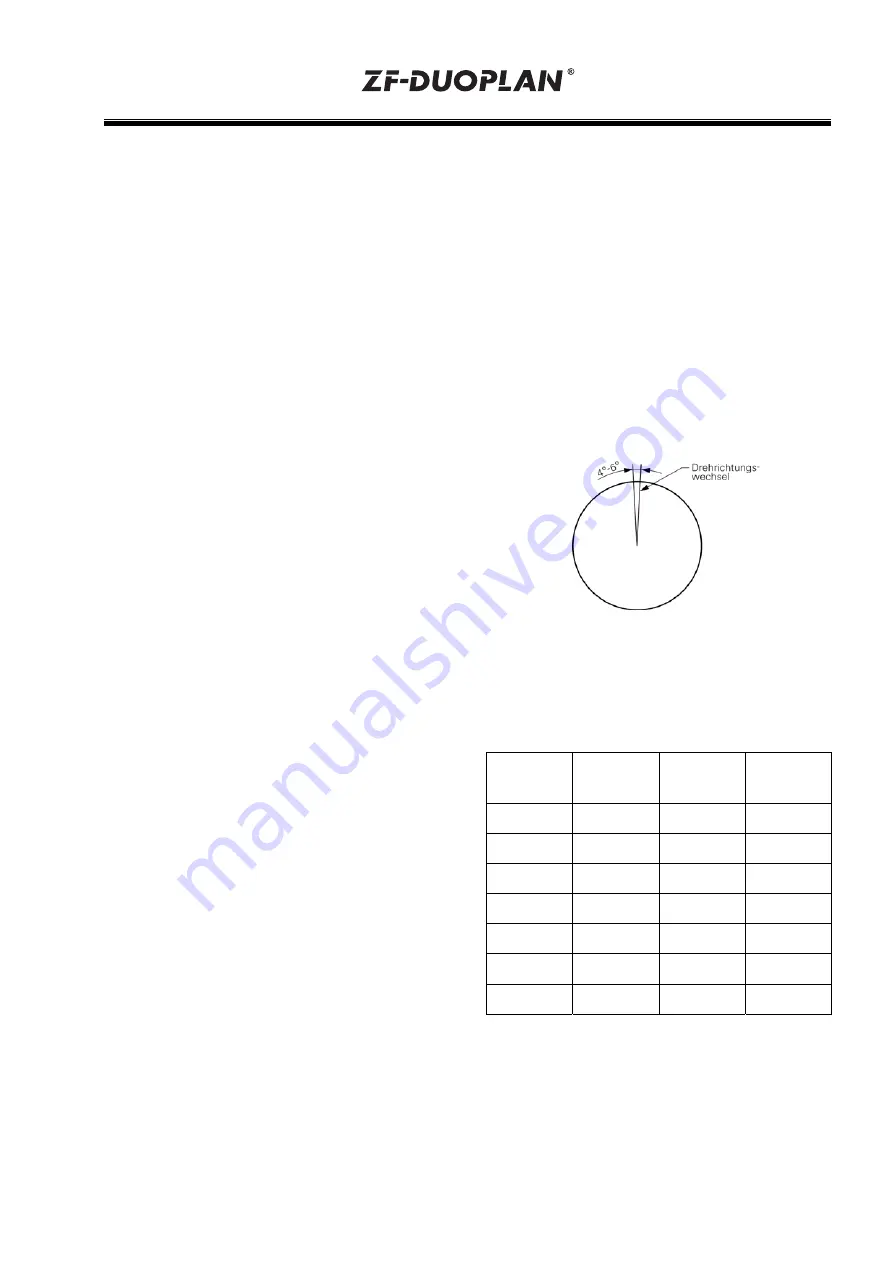
Gearbox shift mechanism:
During transmission stage changeover, the main
spindle motor performs a pendulum motion with a
4° - 6° angle with 1 to 5 changes in rotary
direction per second. Major pendulum motion
may lead to damage at the meshing gears.
In average, this means: n
Mot
= 5°/s = 5° 60/min =
300°/min = 300/360 rpm = 0.83 rpm.
Conversion
Pendulum speed
↔
pendulum rotary motion
Speed
[rpm]
Angle
[°/min]
Time
[sec]
Angle
[°/sec]
0.25 90 3.33 5
0.50 180 1.67 5
1.00 360 0.83 5
2.00 720 0.42 5
3.00 1080 0.28 5
4.00 1440 0.21 5
5.00 1800 0.17 5
The machine optimum is to be determined on the
basis of shift tests in relation to the different
masses and thereto connected drag torques of the
spindle.




























