7
Calibrate the Sensor
Calibration is a measuring procedure in which a calibration object is meas‐
ured. This configures the measuring system and ensures its dimensional
accuracy. During this process, the software determines geometric parame‐
ters, e.g., the position and orientation of each camera, based on recorded
camera images. The software also determines the image characteristics of
the camera lens and camera chip.
These settings are the basis for the software’s computations. Using the cal‐
ibration object’s points in the 2D camera image, the software computes
the points’ 3D coordinates.
It then computes the 3D coordinates back into the 2D camera images. This
results in the reference point deviation (intersection deviation) for the
position of the reference points.
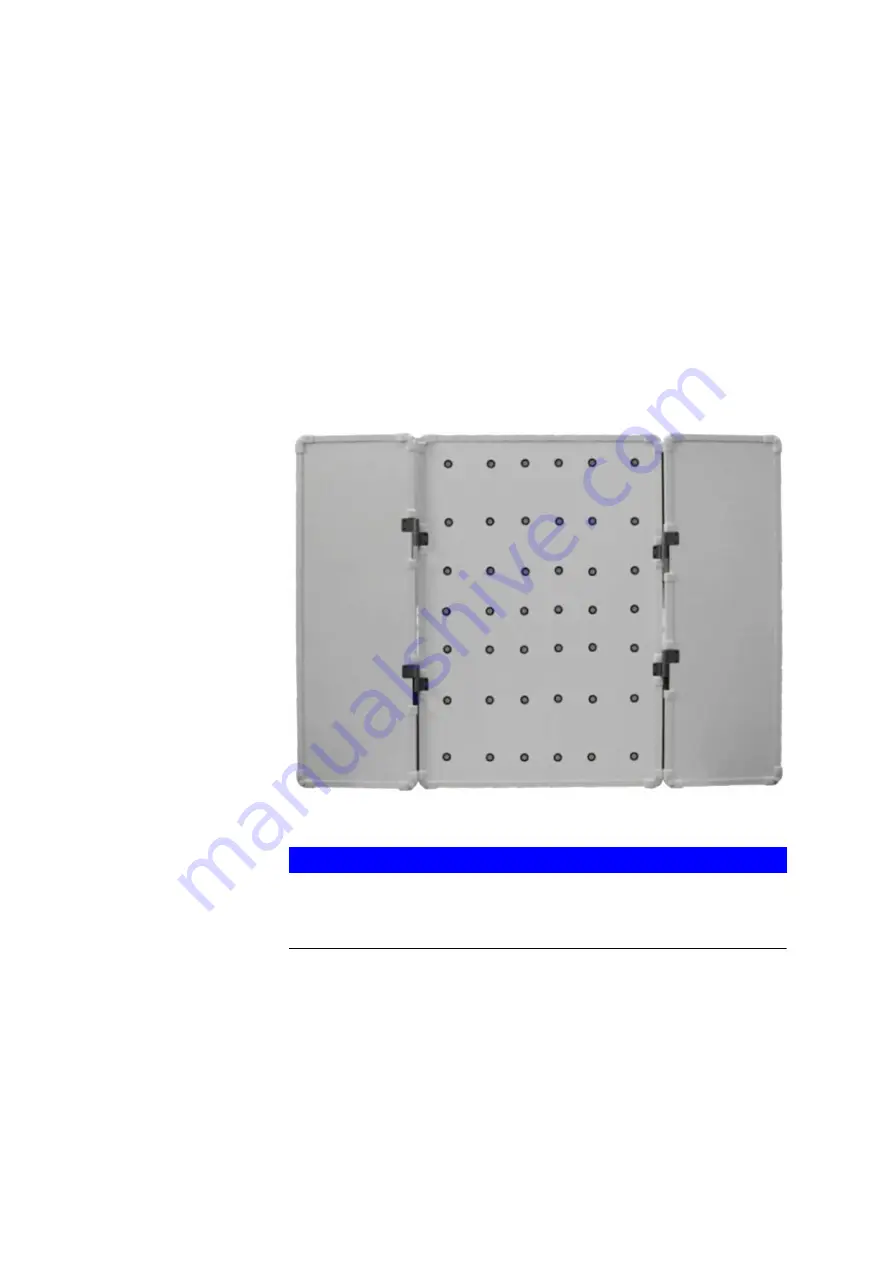
The T-SCAN hawk comes with a calibration object.
Fig. 5: T-SCAN hawk calibration object
NOTICE
Unsuitable calibration objects may impact measuring accuracy.
▶
When calibrating, only use the calibration object intended for your
sensor.
7.1
When is Calibration Necessary?
•
After the sensor is connected to the computer, it needs to be calibra‐
ted.
0000001879_002_EN_30-09-2020
Page 14 (19)





































