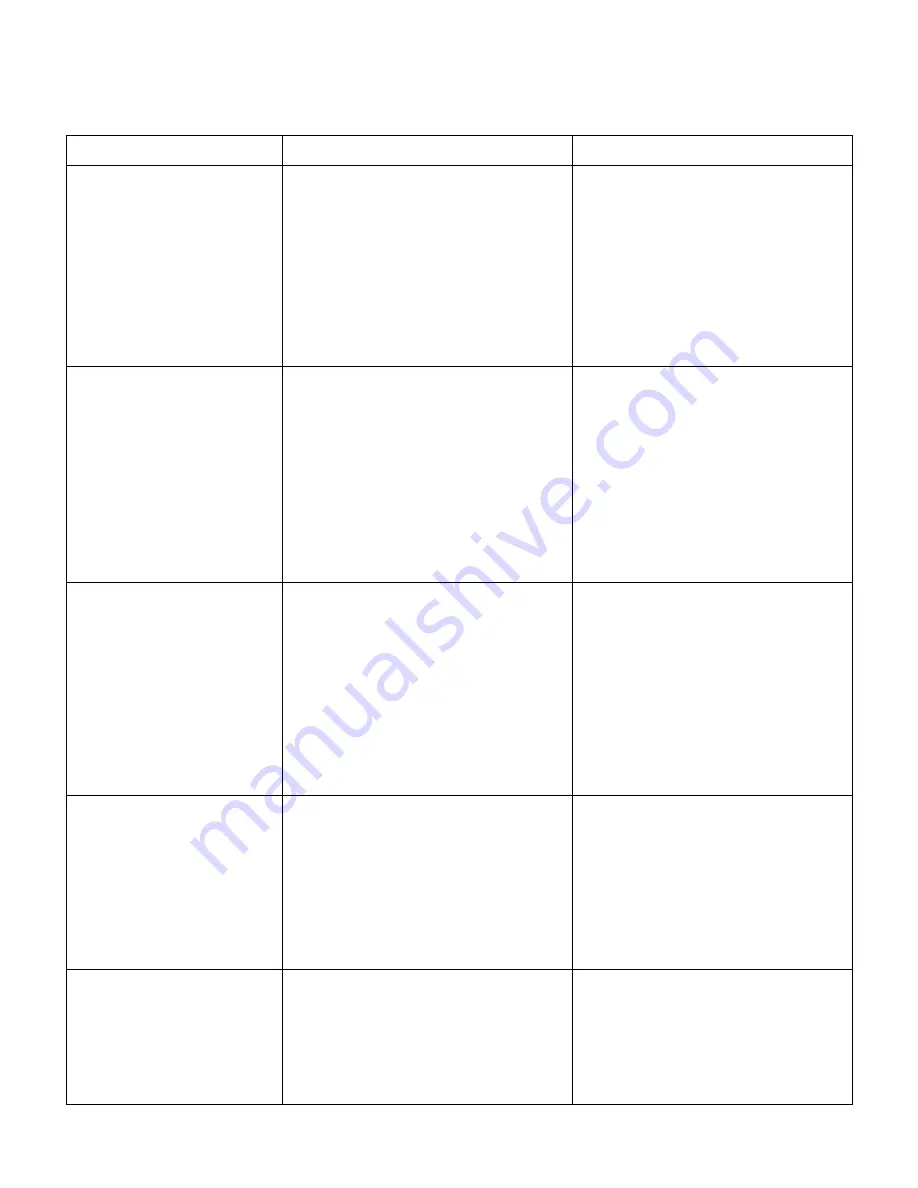
TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART
SYMPTOM
CAUSES
CHECK & CORRECTIVE MEASURE
Units runs OK, but short
cycles on.
1. Check the cause.
2. Differential set too close - widen.
3. (a) Check airflow to the condenser
correct.
(b) Reduce refrigerant charge.
(c) Purge.
4. (a) Fix leak, add refrigerant.
(b) Replace device.
Unit operates long or continu-
ously.
Evaporator ices up.
Head pressure too high.
Head pressure too low.
1. Shortage of refrigerant.
2. Control contacts stuck or frozen
closed.
3. Refrigerated or air conditioned space
has excessive load or poor insulation.
4. System inadequate to handle load.
5. Evaporator coil iced.
6. Restriction in refrigeration system.
7. Dirty condenser.
8. Filter dirty.
1. Restricted airflow.
2. Dirty air filter.
3. Short of refrigerant.
4. Low air volume.
5. Restricted distributor tube.
6. Restricted liquid line/low liquid line
pressure.
1. Refrigerant overcharge.
2. Air in system.
3. Dirty condenser.
4. Malfunction of condenser fan (air-
cooled).
5. Excessive air temperature entering
condenser.
6. Restriction in discharge line.
1.Low ambient temperatures (air-
cooled).
2. Refrigerant shortage.
3. Damaged valves in compressor.
1. Fix leak, add charge.
2. Clean contacts or replace control.
3. Determine the fault and correct.
4. Replace with larger system.
5. Defrost.
6. Determine location and remove.
7. Clean condenser.
8. Clean or replace.
1. Check for dirt or lint on coil.
2. Clean or replace. Advice customer
on periodic cleaning of filter.
3. Check system pressure. Take super-
heat reading. Add refrigerant.
4. Check for dirty air filter or loose belt.
5. Check for warm distributor tube.
6. Check for restriction in lines/improve
liquid line pressure by proper charg-
ing or installing fan cycle switch, etc.
1. Correct the refrigerant charge.
2. Recharge the system after a thorough
triple evacuation.
3. Clean.
4. Check and correct or replace.
5. Check for short circuiting of con-
denser discharge air, correct it.
6. Correct it.
1. Install fan cycling switch, if not pro-
vided. Check the setting and opera-
tion, if provided.
2. Correct the refrigerant charge after
leak testing.
3. Repair/replace the compressor.
1. Overload protector.
2. Thermostat.
3. High pressure cut-out due to:
(a) Insufficient air.
(b) Overcharge.
(c) Air in system.
4. Low pressure cut-out due to:
(a) Undercharge.
(b) Restriction in expansion device.
32











































