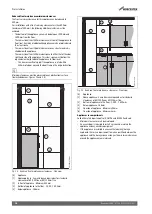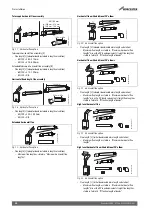
Pre-Installation
29
Greenstar 4000 – 6 720 891 162 (2020/09)
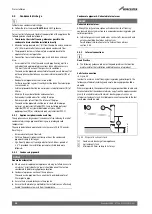
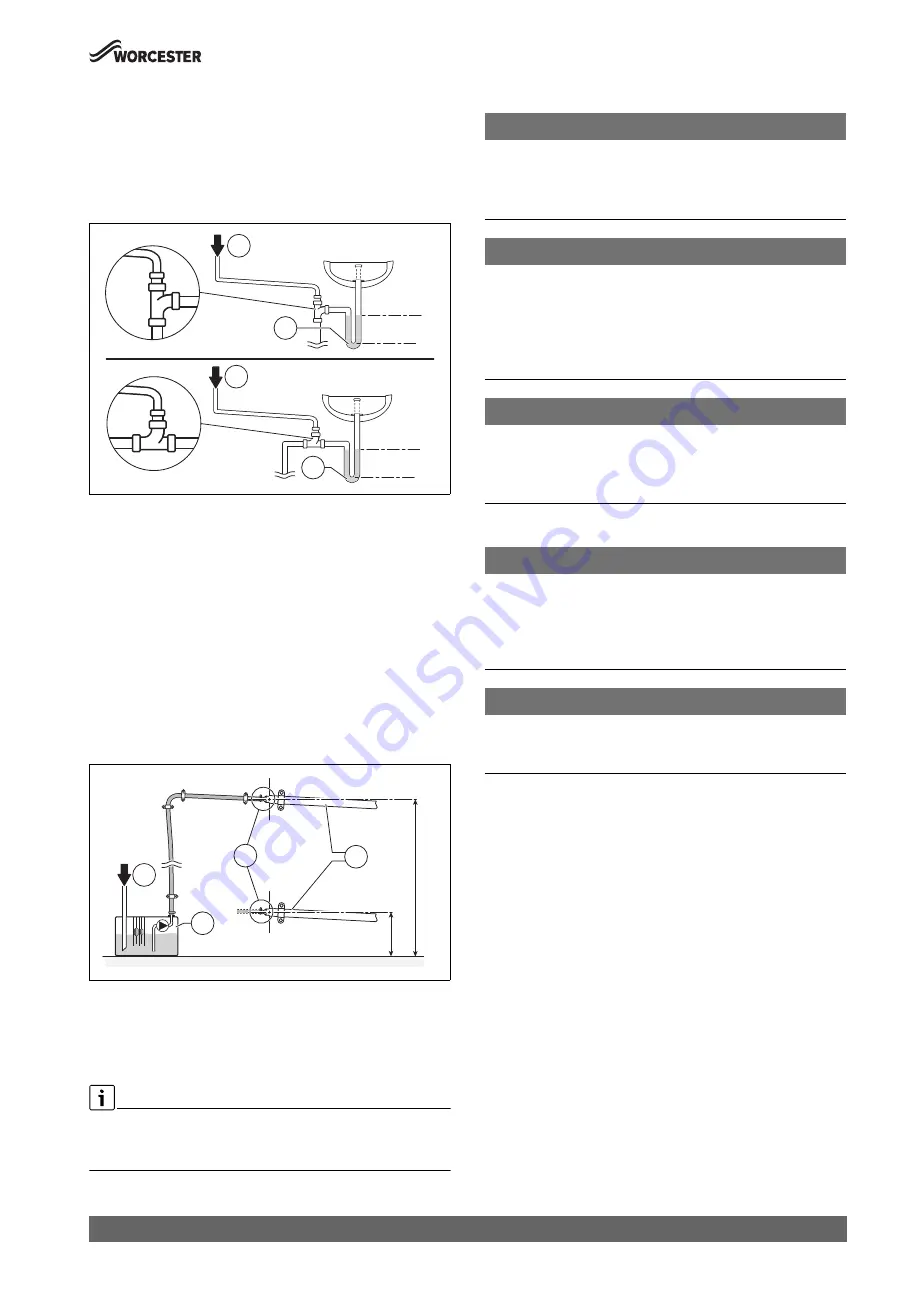
Waste pipe connection
Figure 36
Alternatively if the first option is not possible an internal kitchen,
bathroom or washing machine waste pipe etc. can be used.
Ensure that the condensate drain pipe is connected “down stream” of
the waste trap and that the condensate drain enters into the top of the
pipe using a swept tee.
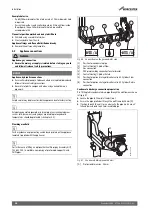
Fig. 36 Waste pipe disposal
[1]
Condensate discharge from appliance
[6]
75mm sink waste trap
Condensate pump
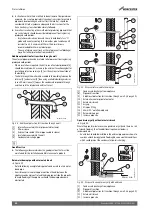
Figure 37
Where direct connection to “gravity discharge” pipework is not
physically possible, or where very long internal runs would be required to
reach a suitable discharge point, condensate should be removed using a
proprietary condensate pump, of a specification recommended by the
condensate pump manufacturer.
• The pump outlet should discharge to a suitable “gravity discharge”
outlet.
– The condensate then flows, by gravity, through the 22mm plastic
pipe to the condensate discharge point.
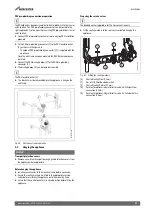
Fig. 37 Condensate pump example
[1]
Condensate discharge from appliance
[7]
Condensate pump
[8]
Pipework transition
[C]
Gravity discharge pipework
Proprietary condensate pump
▶ Ensure minimum and maximum pump lifting heights are followed as
per condensate pump manufacturers instructions.
4.5.4
External connections
NOTICE
Septic tanks
Untreated condensate must not be allowed into septic tanks.
▶ Connection to systems which drain into a septic tank should be
avoided due to the risk of affecting anaerobic bacteria.
NOTICE
Rainwater down pipe or external drain disposal
Untreated condensate must not be allowed to flow into streams or rivers.
▶ A rainwater down pipe or an external drain shall only be used for
condensate disposal if the down pipe or external drain is connected
to a combined foul and rainwater drainage system.
▶ Refer to BS 6798 for more information on condensate disposal.
NOTICE
Grey water recovery system
Contamination of recovered water
▶ Condensate disposal shall not be allowed into a grey water recovery
system that is intended for re-use.
External disposal considerations
NOTICE
Freezing conditions
Frozen condensate will block the condensate drain pipe and stop the
appliance from running.
▶ Pipe lengths should be kept to a minimum and routed as vertically as
possible.
NOTICE
Condensate waste disposal
▶ Care should be taken when siting a soak-away to avoid causing
damage to existing services and building footings.
If no other discharge method is possible then the use of an externally run
condensate drainage pipe terminating at a suitable foul water discharge
point, or purpose-designed soak away, may be considered. If this
method is chosen then the following measures should be adopted:
▶ The external run be kept as short as possible and ideally should not
exceed three metres.
Additional precaution against freezing must be taken if the external
pipe run does exceed three metres.
▶ The pipe should be run internally as far as possible before going
externally and the pipe diameter should be increased to a minimum
internal diameter (ID) of 30mm before it passes through the wall to
the exterior.
▶ The hole through the wall for the condensate pipe should be sleeved
and be sealed to the building fabric on the internal and external face
using a suitable building material.
▶ The external pipe should take the shortest and least exposed route to
the discharge point, and should "fall" as steeply as possible away
from the appliance, with no horizontal runs in which condensate
might stand.
▶ The use of fittings, elbows etc. should be kept to a minimum and any
internal burrs on cut pipework should be removed so that the internal
pipe section is as smooth as possible.
▶ All external pipe drainage will be improved if the end is cut at 45° as
opposed to a straight cut.
0010012767-002
75mm
min.
75mm
min.
6
6
1
1
0010023656-002
Min.
Max.
1
8
C
7