Flicker Frequency
Flicker Frequency is the flicker frequency of lamp typically caused by the driver and
supplied AC current.
Flicker Percentage (PF)
Modulation Depth (MD)
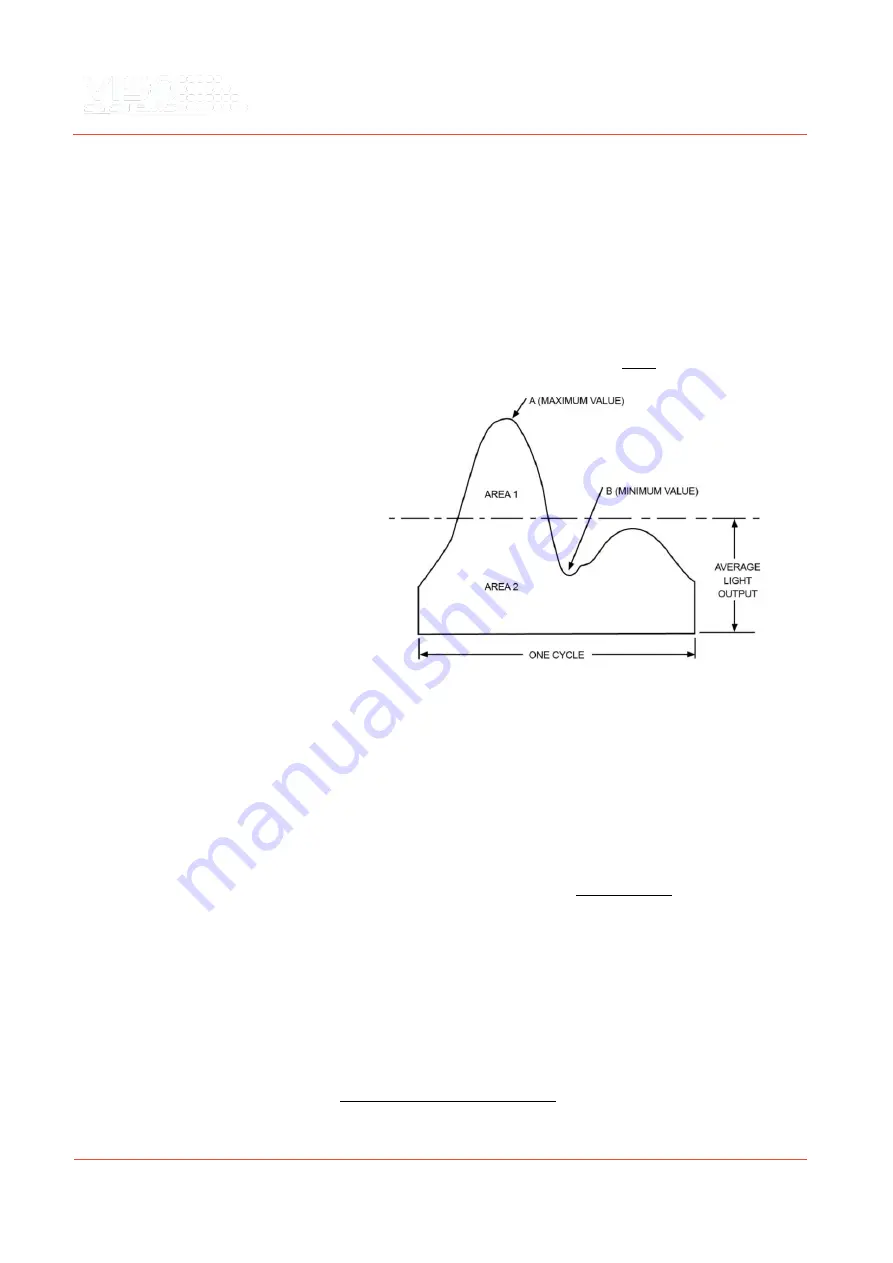
Flicker percent is a relative measure of the cyclic variation in the output of a light
source (i.e., percent modulation). Sometimes this is also referred to as the
“modulation index” (as a fraction between 0 and 1, not percent). From the figure
1
below:
𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑓𝑙𝑖𝑐𝑘𝑒𝑟 = 100 ∙
𝐴 − 𝐵
𝐴 + 𝐵
%
Flicker Index (FI)
According to CIE S 017:2020, 17-22-094 (CIE 2020) the flicker index (symbol
I
F
) is the
quotient of the above-average luminous energy to the total luminous energy over a
period of time.
Hence, the Flicker Index is a “relative measure of the cyclic variation in the output of
various sources at a given power frequency. It considers the waveform of the light
output as well as its amplitude”
. The flicker index assumes values from 0 to 1.0, with
0 for steady light output. Higher values indicate an increased possibility of noticeable
lamp flicker, as well as stroboscopic effect. Again, from the figure above:
𝐹𝑙𝑖𝑐𝑘𝑒𝑟 𝐼𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑥 =
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 1
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 1 + 𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 2
New flicker metrics
Flicker Index and Flicker Percent are not suitable to describe the effect of light
modulations of human perception. E.g., 100% flicker at 1,000 Hz flicker frequency
will result in a very high flicker index but at 1,000 Hz humans will generally not be
affec
ted by flicker, so ‘Percent Flicker’ and ‘Flicker Index’ will not describe human
perception of stroboscopic effects. The latest research in what is collectively referred
to as 'Temporal Light Artifacts' distinguishes three different effects:
flicker
(static
light sources),
stroboscopic effects
(moving light sources) and
phantom array effects
1
The IESNA Lighting Handbook, 9th Edition, Mark S. Rea, 2000













