Solar System Design Guide
6020 457 - 01
70
Swimming Pool Heating System with Heat Exchanger and Collectors
(continued)
Indoor pools
Indoor pools generally have a higher target temperature
than outdoor pools and are used throughout the year. If,
over the course of the year, a constant pool temperature
is required, indoor pools must be heated in dual mode.
To avoid sizing errors, the energy demand of the pool
must be measured. For this, suspend reheating for 48
hours and determine the temperature at the beginning
and end of the test period. The daily energy demand can
therefore be calculated from the temperature differential
and the capacity of the pool. For new projects, the heat
demand of the swimming pool must be calculated. For
this sizing calculation, the user must select a location
from the list (see pages 64 and 65).
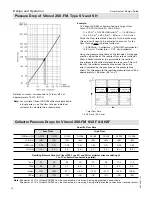
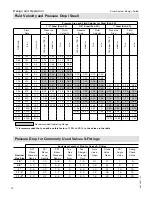
Calculation example for Vitosol 200-FM
Pool surface area:....................387 ft
2
(36 m
2
)
Average pool depth:.................5 ft. (1.5 m)
Pool capacity:.........................14,300 USG (54,126 L)
Temperature loss per day:........1.8°F (1°C)
Calculation example for Vitosol 200-FM
Number of days per month: ...................30 days in June
Volume of indoor pool: .................................... 54,126 L
Density of water: ................................................1 kg/L
Specific heat of water: ................................4190 J/kgºC
Temperature loss of pool water per day: ...................1°C
System efficiency: .................................................0.42
Solar radiation (Boston): .........................22.1 MJ/m²/day
Collector absorber area (Vitosol 200-FM): ............ 2.32 m²
Nc = ((30 days x 54,126 L x 1 kg/L x 4190 J/kgºC x
1ºC) ÷ 0.56) ÷ (22.1 MJ/m²/day x 1,000,000 x
30 days) ÷ (2.32m²) = 7.9x Vitosol 200-FM
Note:
To prevent overheating it is recommended to
round the quantity of collectors down to the
next whole number. For this example, 8x Vitosol
200-FM collectors would be the recommended
number of collectors to satisfy the DHW load for
the month of June.
Number of days in each month
January = 31
July = 31
February = 28
August = 31
March = 31
September = 30
April = 30
October = 31
May = 31
November = 30
June = 30
December = 31
Nc = ((Ndays x Vpool x p x Cp x
∆
T) ÷ Se) ÷
(Gt x 1,000,000 x Ndays) ÷ (Ca)
Where:
Nc = Number of collectors required to meet 100% of
the pool heating load
Ndays = Number of days per month (see table below)
Vpool = Volume of indoor pool (Liters)
p = Density of water (1 kg/L)
Cp = Specific heat of water (4190 J/kgºC)
∆
T = Temperature loss of pool water per day (ºC)
Se = System efficiency in decimal format
(assume 70% collector efficiency x 80% balance
of system efficiency =56% or 0.56)
Gt = Solar radiation (MJ/m²/day)
*Note: 1 kwh = 3.6 MJ or 3,600,000 Joules
Ca = Collector absorber area (Vitosol 200-FM = 2.32 m²)
Design and Operation