23
Installation info
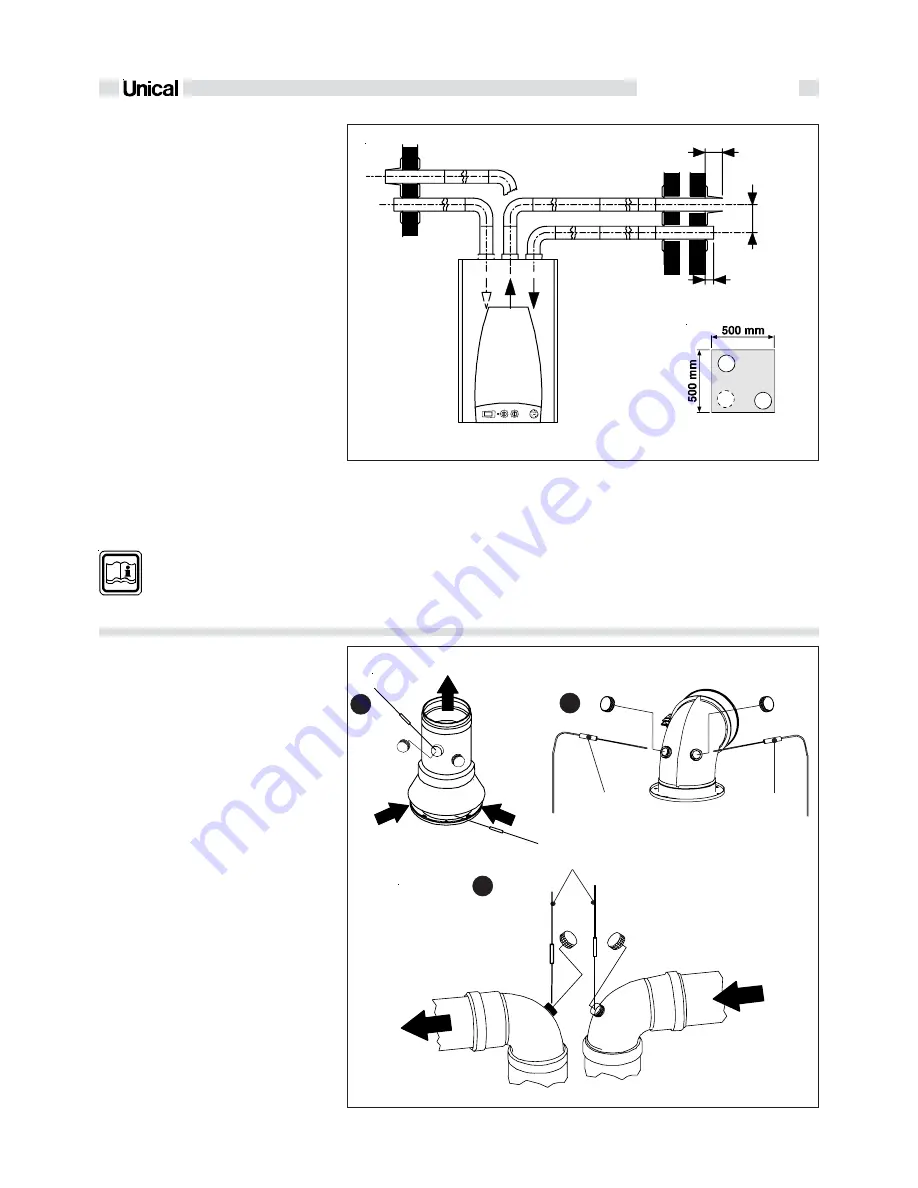
fig. 22
fig. 21
135
45
C
2
1
250 min.
Example of check using wide radius
bends:
-
17 mt duct Ø 80 x 2 =
34 Pa
-
2x90° Ø 80 long radius bends 2x4 =
8 Pa
-
horizontal Ø 80 air inlet terminal =
3 Pa
-
horizontal Ø 80 terminal =
5 Pa
Tot. pressure loss = 50 Pa
1
2
A
Air
inlet
1
Smoke
outlet
B
2
Example N.2
CALCULATION OF PRESSURE LOSSES
FOR DISCHARGE AND SUCTION DUCTS
Bear in mind the following parameters when
calculating pressure losses:
-
for each metre of duct with Ø 80 (both
suction and discharge) the pressure loss
is 2 Pa;
-
for each 90° Ø 80 (R=D) bend with long
radius, the pressure loss is 4 Pa;
-
for each 90° Ø 80 (R=½ D) bend with
short
radius, the pressure loss is 14 Pa
-
for the Ø 80 L = 0.5 m horizontal air inlet
terminal, the pressure loss is 3 Pa;
-
for the Ø 80 L = 0.6 m horizontal
discharge end section, the pressure loss
is 5 Pa;
NB: These values refer to dis-
charges through original UNI-
CAL non-flexible and smooth
ducts.
Example N.2
Primary air suction from perimeter wall and
flue gas discharge from the same outside pe-
rimeter wall.
I
t is not allowed to position the 2 termi-
nals in opposite walls,
Maximum allowable pressure loss:
50 Pa
2.2.11-
MEASUREMENTS OF
COMBUSTION EFFICIENCY
Ducts Ø 80 type B22 (C)
Coaxial ducts (A)
Dual ducts Ø 80 (B)
To determine combustion efficiency the fol-
lowing measurements must be made:
-
the combustion air temperature measured
in hole
2
(see fig. 22).
-
the flue gas temperature and CO
2
% mea-
sured in hole
1
(see fig. 22).
Make these measurements with the boi-
ler running in a steady state condition.
Air
inlet
Smoke
outlet
Analyser
probe
Analyser
probe
Analyser
probe
Analyser
probe














































