SECTION 8: BASIC WELDING TECHNIQUE
8.01 Setting of the
Fabricator
The
Fabricators
Power Source ha
s
two control settings that have to balance. These are
the
Wirespeed control and the Voltage Control switches. The welding current is
determined by the Wirespeed control, the current will increase with increased
Wirespeed, resulting in a shorter arc. Less wire speed will reduce the current and
lengthen the arc. Increasing the welding voltage hardly alters the welding current level,
but lengthens the arc. By decreasing the voltage, a shorter arc is obtained with little
change in welding current.
When changing to a different electrode wire diameter, different control settings are
required
, a
thinner electrode wire needs more Wirespeed to achieve the same current
level.
A satisfactory weld cannot be obtained if the wirespeed and voltage switch settings
are not adjusted to suit the electrode wire diameter and dimensions of the work piece.
If the Wirespeed is too high for the welding voltage, “stubbing” will occur as the wire
dips into the molten pool and does not melt. Welding in these conditions normally
produces a poor weld due to lack of fusion. If, however, the welding voltage is too
high, large drops will form on the end of the electrode wire, causing spatter. The
correct setting of voltage and Wirespeed can be seen in the shape of the weld deposit
and heard by a smooth regular arc sound.
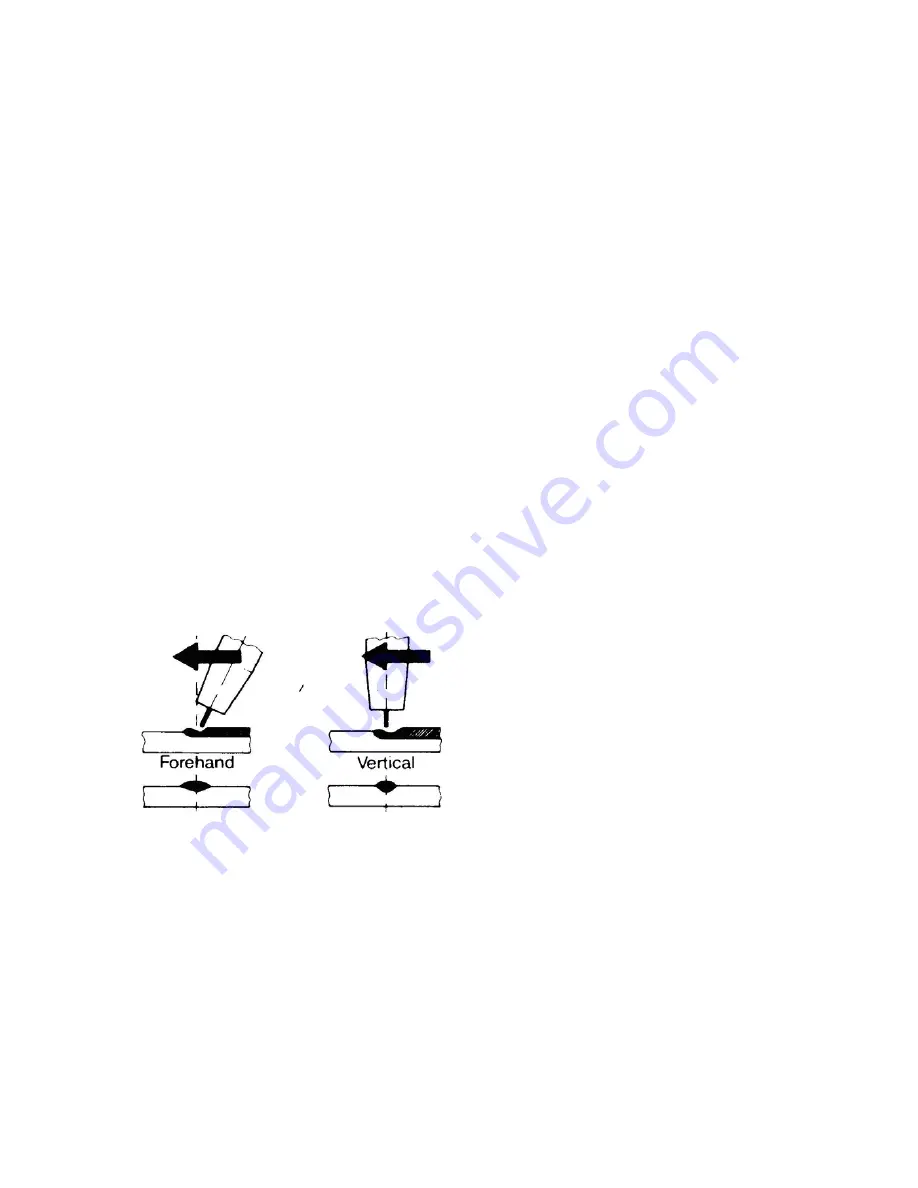
8.02 Position of MIG Torch
MIG torch angle to the weld has an effect on the width of the weld run. Refer to figure
17.
Figure 2
4
.
8.03 Distance of the MIG Torch Nozzle to the Work Piece
The electrode stick out from the MIG Torch nozzle should be between 2.0mm (5/64”)
and
5.0mm. (13/64”) This distance may vary depending on the type of joint that is being
welded.
8.04 Travel Speed
Speed at which a weld travels influences the width of the weld and penetration of the
welding run.
8.05 Electrode Wire Size Selection
The choice of electrode wire size in conjunction with shielding gas used depends on:
a) Thickness of the metal to be welded,
b) Type of joint,
39
Summary of Contents for C/W VFE 4C HS III
Page 10: ...Page left blank intentionally 4...
Page 13: ...1 04 SYMBOL LEGEND Figure 2 7...
Page 27: ...This page has been left blank intentionally 21...
Page 53: ...This page has been left blank intentionally 47...
Page 54: ...SECTION 11 SPARE PARTS 11 01 Parts Description Fabricator 250C 320C Figure 26 48...
Page 57: ...11 02 Parts Description Fabricator 320S 400S Figure 27 51...
Page 62: ...11 04 Parts Description Fabricator 500S Figure 29 56...
Page 69: ...12 02 Power Source Schematic Fabricator 320S III 400S III Figure 33 63...
Page 70: ...12 03 Power Source Schematic Fabricator 500S III Figure 34 64...
Page 71: ...12 04 Wire Feed Unit Schematic VFE 4C III VFE 4C HS III WFU Figure 35 65...
Page 73: ...This page has been left blank intentionally 67...
















































