1-877-420-1330
Quest DRY 180 Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions
9
www.QuestHydro.com
quest
quest
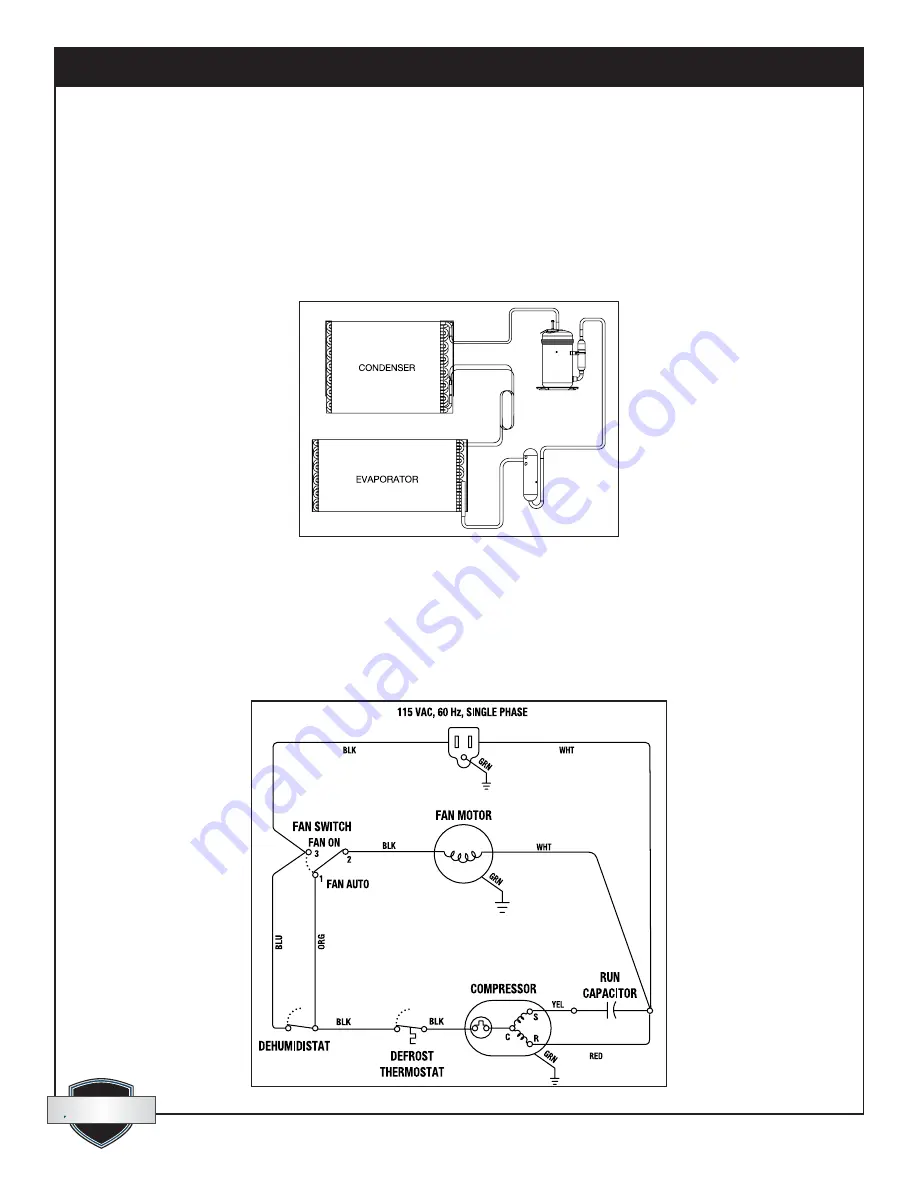
8.1 Technical Description
The Quest Dry 180 uses a refrigeration system similar to an air conditioner’s to remove heat and moisture
from incoming air and add heat to the air that is discharged. Hot, high pressure refrigerant gas is routed from
the compressor to the condenser coil. The refrigerant is cooled and condensed by giving up its heat to the air
that is discharged from the dehumidifier. The refrigerant liquid then passes through capillary tubing which
cause the refrigerant pressure and temperature to drop. It next enters the evaporator coil where it absorbs heat
from the incoming air and evaporates.
The evaporator operates in a flooded condition, which means that all the evaporator tubes contain liquid
refrigerant during normal operation. A flooded evaporator should maintain constant pressure and temperature
across the entire coil, from inlet to outlet. The mixture of gas and liquid refrigerant enter the accumulator after
leaving the evaporator coil. The accumulator prevents any liquid refrigerant from reaching the compressor. The
compressor evacuates the cool refrigerant gas from the accumulator and compresses it to a high pressure and
temperature gas to repeat the process.
Figure 13: Quest Dry 180 refrigeration system.
Figure 14: Wiring Diagram.