72
5.3
Fan Speed Control
This demo helps users quickly understand how to set the MAX6650 chip from the FPGA
to control the fansink. The MAX6650 chip can set or retrieve the RPM of the fansink. It
can also monitor if there is any unexpected error and determine which type of error it is.
The following section will save lots of time for the development of user application.
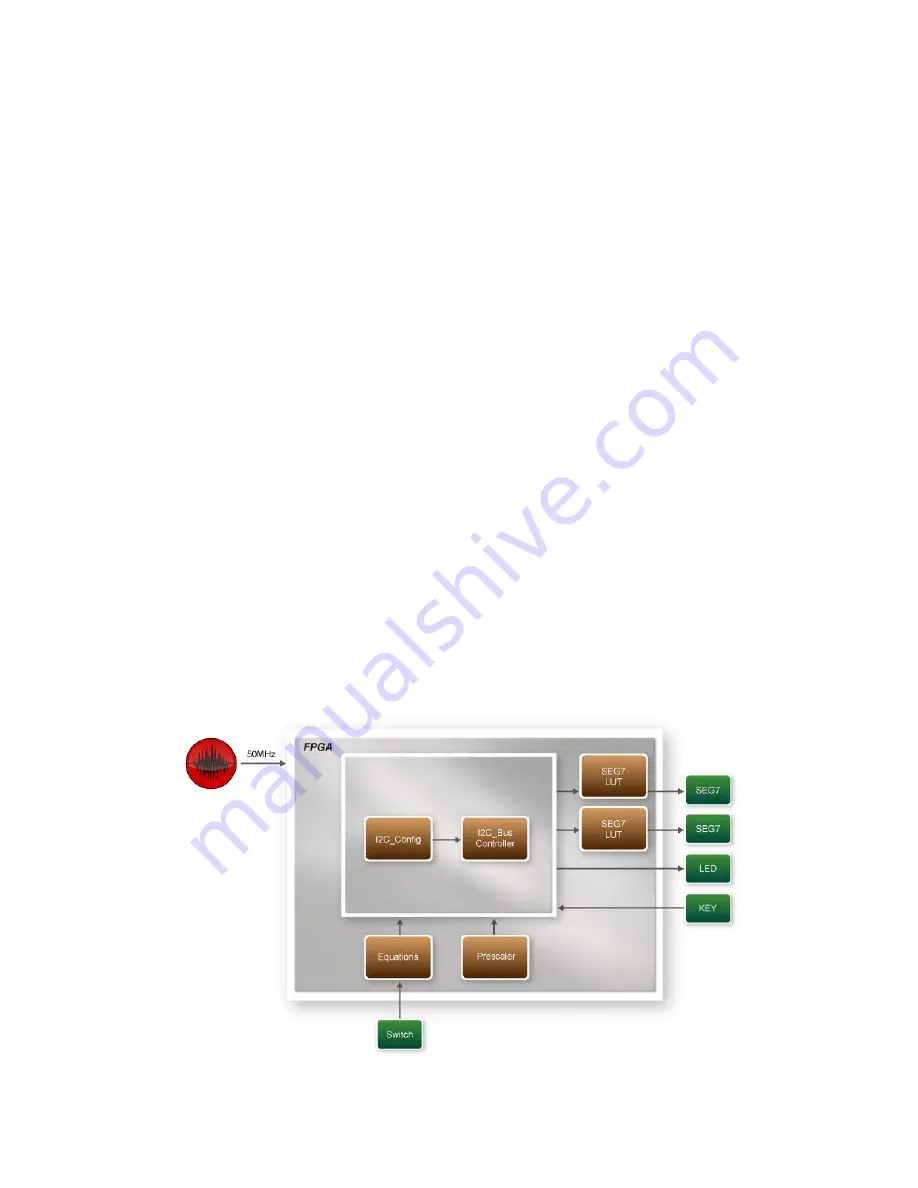
System Block Diagram
Figure 5-16
shows the system block diagram of this demo. It is necessary to configure
the MAX6650 chip prior upon the initialization of fansink control. The MAX6650 chip
uses standard I2C protocol for communication. The functions I2C_Config and
I2C_Bus_Controller set and monitor the RPM of the fansink, respectively. A pre-scaler
is used as frequency divider for the clock frequency of I2C. Users need to calculate the
frequency based on the equations from the datasheet to control the RPM of the fansink.
There are three equations in the datasheet and this demo uses one of them. For other
equations, please refer to the datasheet MAX6650-MAX6651.pdf in the system CD.
The Switch[0] controls the RPM in this demo. When the Switch[0] is set to 0, the speed
is around 2000 RPM. The speed would reach about 5000 RPM if the Switch[0] is set to
1. It would take 10 ~ 30 secs as the buffer time for the conversion. If an error is detected,
the LED would lit. Users need to press KEY[1] to reset the LED by turn it off.
Summary of Contents for TR10a-HL
Page 1: ...1...
Page 3: ...3...
Page 71: ...71 Figure 5 14 Si5340A Demo Figure 5 15 Si5340B Demo...
Page 82: ...82 Figure 6 3 Progress and Result Information for the QDRII Demonstration...
Page 107: ...107...
















































