Glossary 3
I/O MAP
An I/O (Input/Output ports) map is a list of all special hardware circuits used by the computer to communicate with
external devices. They are simply a special type of memory location that can be accessed only by means of the IN and
OUT instructions. It is possible to have up to 65 536 different I/O devices attached to the system since the I/O port
addresses are 16-bit numbers. Actually, most I/O devices (disk drive controller, video display controllers, etc.) require
more than one I/O port to control them.
IRQ
(INTERRUPT REQUEST)
Hardware channels over which devices such as I/O ports, disk drives, and the keyboard can send interrupts to the
processor. They are built into the computer’s internal hardware and are assigned different priority levels so the
processor can determine the relative importance of incoming requests for service. There are 16 IRQs in ISA systems.
See Interrupt.
ISA
(INDUSTRY STANDARD ARCHITECTURE)
In reference to IBM PC AT compatible computers, it is the definition of the standard bus. In other words ISA is the
Industrial Standard Architecture expansion bus built into the IBM PC AT computer.
MEMORY MAP
A technical reference that shows the entry point and marks the blocks of memory that are reserved for specific
functions.
MEZZANINE CARD - MEZZANINE BOARD
A peripheral card which uses the PC/104 or the 62-pin XT extension header connectors on TEKNOR boards.
Mezzanine Board allows to assembly a complete computer without passive backplane.
PASSIVE BACKPLANE
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) populated mostly with passive electronic components (connectors, resistors...)
equipped with connectors that accept different types of Plug-in Electronic boards (SBC, Video Board, I/O Board...).
The main purpose of the Passive Backplane is to serve as an interconnection medium for the different Plug-in boards
installed in a computer system. The backplane is also generally used to supply power to the different Plug-in boards.
REAL-TIME CLOCK
(RTC)
It is needed for software compatibility and it has no direct relationship with the ISA bus. It provides time and date
information.
RS-232 OR RS-232C
A standard which defines the physical and electrical serial interface used to connect data communications equipment.
This is the most commonly used interface, especially between modems and computers.
There are two interfaces : DTE (Data Terminal Equipment), used by computers, and DCE (Data Communications
Equipment), used by modems.
Summary of Contents for TEK-AT4L Plus
Page 7: ...PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW 2 ONBOARD SUBSYSTEMS...
Page 9: ...Product Overview 1 2 TEK AT4LPLUS Block Diagram...
Page 26: ...Installing Devices 6 3 CONNECTOR LOCATION...
Page 35: ...Setting Jumpers 8 3 JUMPER LOCATIONS...
Page 36: ...Setting Jumpers 8 5 TABLE 8 1 Jumper Settings W1 W11...
Page 37: ...Setting Jumpers 8 6 TABLE 8 2 Jumper Settings W12 W19 W26...
Page 38: ...Setting Jumpers 8 7 TABLE 8 3 Jumper Settings W20 W25 SW1 SW2...
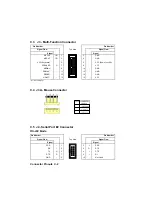
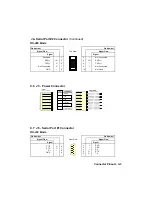
Page 41: ...APPENDICES A PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS B BOARD DIAGRAMS C CONNECTOR PINOUTS...
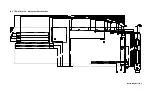
Page 43: ...Board Diagrams B 1 B 1 TEK AT4LPLUS Assembly Diagram Top View...
Page 44: ...Board Diagrams B 3 B 2 TEK AT4LPLUS Mounting Holes...
Page 45: ...Board Diagrams B 5 B 3 TEK AT4LPLUS Mechanical Specifications...