699-41-20.1
-
5 -
1
Understanding the system set-up and functionality
1.1
System philosophy
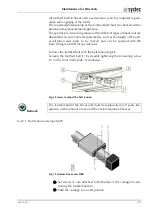
DriveSets are systems with kinematics (with linear axes and rotary mod-
ules) and complete controller electronics.
They can be operated either autonomously or as intelligent subsystems
together with a master computer.
The systems have been constructed according to the newest state of the
art, with strong emphasis on high reliability and low maintenance.
The systems and components are subjected to extensive and strict single
tests, so they require only minimum maintenance when properly in-
stalled and operated within the warranted parameters
DriveSets are divided into four parts:
linear axes or rotary modules
motors
wiring
a Xemo controller
1.2
Linear axes, rotary modules
The linear axes or rotary modules constitute the mechanical structure
with which corresponding motions can be carried out. The linear axes
can be driven either by a spindle or a cogged V-belt. In addition, linear
motors are also used. Rotary modules, designed as turntables, consist in
as a rule of a plate and a gearbox with motor. Inductive proximity
switches or roll-switches for trajectory limitation and reference-point de-
termination are attached to the linear axes. As a rule, two end switches
and a reference switch are located on each axis. In addition, optional
drag chains can be attached.
1.3
Motors
1.3.1
Motors on Xemo R/S Compact Controllers
On DriveSets with Xemo R/S Compact Controllers 2-phase stepping mo-
tors are deployed. These are connected to the linear axes directly by
couplers or by way of cogged V-belts or other gearboxes.
The stepping motors are distinguished by:
torque
revolutions per minute
number of terminals (50 or 100)
operating voltage (24 V/48 V)
mechanical dimensions