DF3/FF3 MANUAL
19
118018-001
Rev E
ASSEMBLY TITLE
ASSEMBLY DRAWING NO.
SCHEMATIC DRAWING NO.
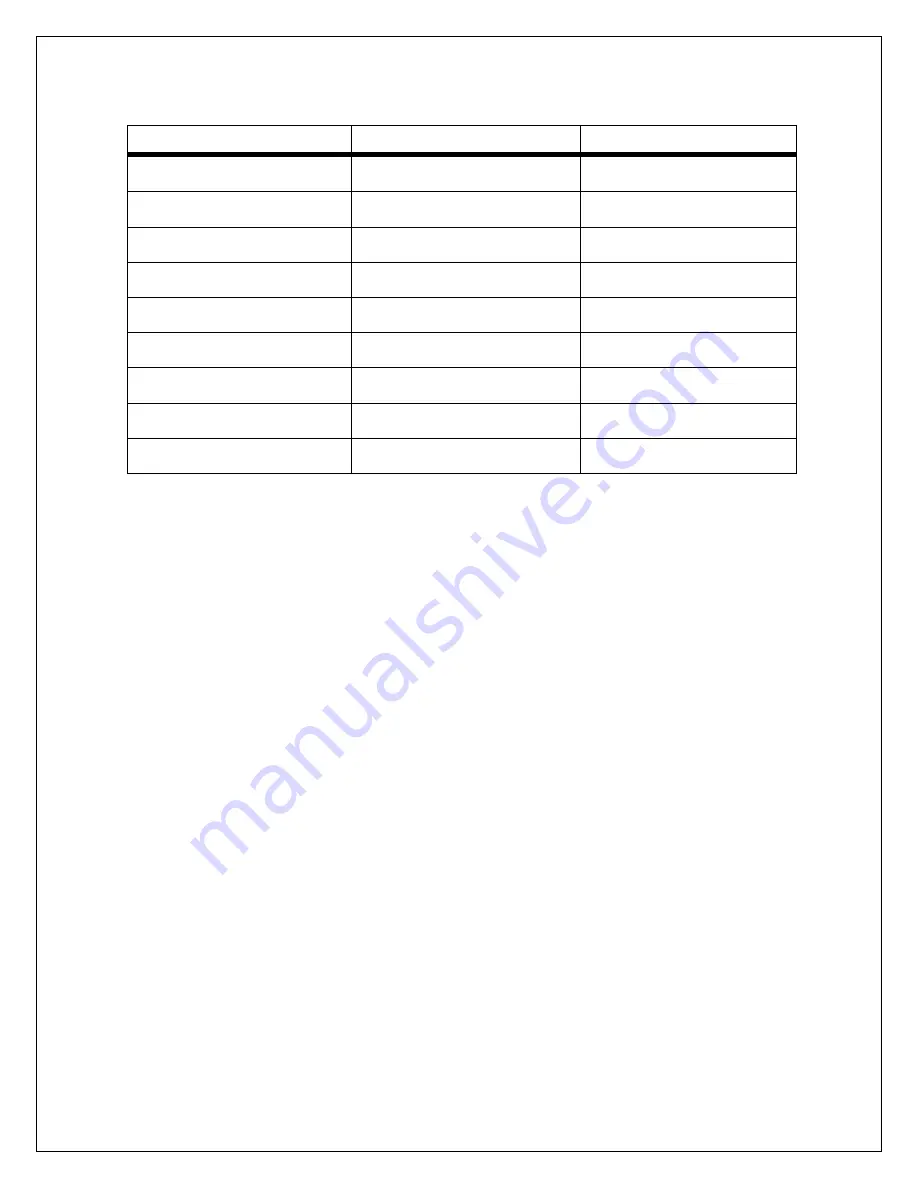
DF3 Chassis
403804-001
440469-007
FF3 Chassis
403805-001
440469-008
IGBT PWB
405102-001
440785-001
System Control PWB
450008-TAB
440716-001
High Voltage Assembly (DF3)
403732-001
440461-001
High Voltage Assembly (FF3)
403733-001
440461-002
Front Panel Assembly
403789-TAB
440443-TAB
Rear Panel Interface PWB
450001-TAB
440500-TAB
Filament Power PWB
404450-TAB
440461-001
Table 4.1 DF3/FF3 MAIN ASSEMBLIES
When K1 is energized, voltage is applied to CR1.
CR1 is an isolated diode power module. It
contains the rectifier diodes used for line voltage
rectification. K1 voltage also supplies power to
fans used throughout the chassis for cooling
purposes. The output of CR1 is connected to a
capacitor filter. Capacitor C1 is initially charged
through a charging resistor. This resistor is
located on the IGBT PWB.
Approximately 1 second after K1 contactor
closure occurs, a relay is energized to short the
charging resistor. This relay is K2. The DC
voltage on C1 is approximately 1.4 times the input
voltage. This DC voltage is supplied to the high
frequency inverter through L2, L3, on the filter
cap assembly. These inductors provide isolation
for the high frequency inverter if a cross
conduction or “shoot thru” occurs. Hence, L1 and
L2 are termed shoot thru chokes.
The IGBT PWB provides a variety of control and
diagnostic functions. R13, R14 are the charging
resistors previously described. These resistors
limit the initial charging current for the capacitors
used for lone rectification. U1 and its associated
circuitry monitor the voltage across the charging
resistor. If any abnormal conditions appear,
circuitry will shutdown the power supply. R38 is
a bleeder resistor, which is used to discharge the
filter capacitor. DS1 provides visual indication
when DC voltage is present. This indicator
should not be relied on for confirming the
presence or absence of the DC voltage. Integrated
circuits provide logic control for AC fault
conditions, contactor control and relay control.
4.3
INVERTER
The inverter is a series resonant, series loaded
topology. A patented control scheme is used for
regulating the power generated from the inverter.
Q1 and Q2 are high speed dual IGBT. These
devices provide high frequency switching to
control the resonant current flow. The typical
resonant operating period is approximately
20uSeconds. The gate control for the switching
devices is provided by the IGBT PWB. VCO1
and VCO2 signals are generated by the SYSTEM
CONTROL PWB. The IGBT PWB provides the
required gate pulse width and phase control.
4.4
HIGH VOLTAGE
TRANSFORMER
The output of the High Frequency Resonant
Inverter is connected to the primary of the High
Voltage Transformer. The High Voltage
Transformer is a step up type. Typical secondary
voltages are in the range of 1kV to 4.5kV
depending upon output voltage ratings.






















