C905
1222-9526 rev. 1
FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
FU
N
C
T
IO
N
A
L O
V
E
R
V
IE
W
Technical Description
CODEC Overview
The CODEC is encoding analog audio signals and analog voice signals into digital signals
using Analog to Digital converters (ADCs). This is done in the coder section of the
CODEC, also named the TX path (transfer section). The CODEC is also decoding digital
audio signals and digital voice signals into analog signals using DACs. This is done in the
decoder section of the CODEC, also named the RX path (receiver section).
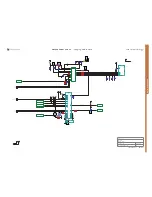
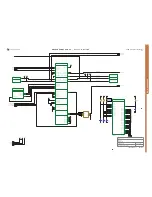
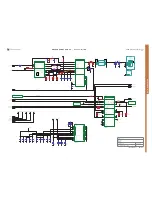
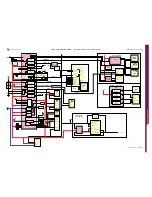
CODEC Block Schematic:
CODEC CCO Voltage Source
There is an internal voltage source CCO that provides the necessary drive current for
electret microphones. The voltage source is I²C programmable to 2.2 V or 2.4 V. The
source can be disabled during standby. A typical use case with a microphone connected
to MIC1 and the CCO is shown in picture below.
Earphone Amplifier
The earphone amplifiers (BEARP and BEARN) are mainly intended to be differentially
configured and drive a low impedance dynamic transducer (earpiece) but they can also
be single ended configured. The BEARP and BEARN amplifiers can be powered down by
the I2C. The amplifiers can exhibit high impedance to 1.4V or low impedance to ground
when powered-down. Fifty-one gains are available for BEARP and BEARN: from +15dB
down to –60dB in 1.5dB steps. When the BEARP and BEARN outputs are operating in
differential mode, an I²C selectable bit must invert one of the inputs.
Speaker Amplifier
The speaker amplifiers, SPKRP and SPKRN, are intended to drive a low impedance (8
Ω
)
speaker in a differential mode or to be used as a stereo configured line output amplifier
supporting external high power amplifiers. The output buffer shall exhibit low impedance
to ground when powered-down and the current consumption shall be minimal. When the
SPKRP and SPKRN outputs are operating in differential mode, an I²C selectable bit must
invert one of the inputs.
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
91
(124)