User Manual – SEFRAM 53X2DC
47
Using the vertical cursors
Procedure
1.
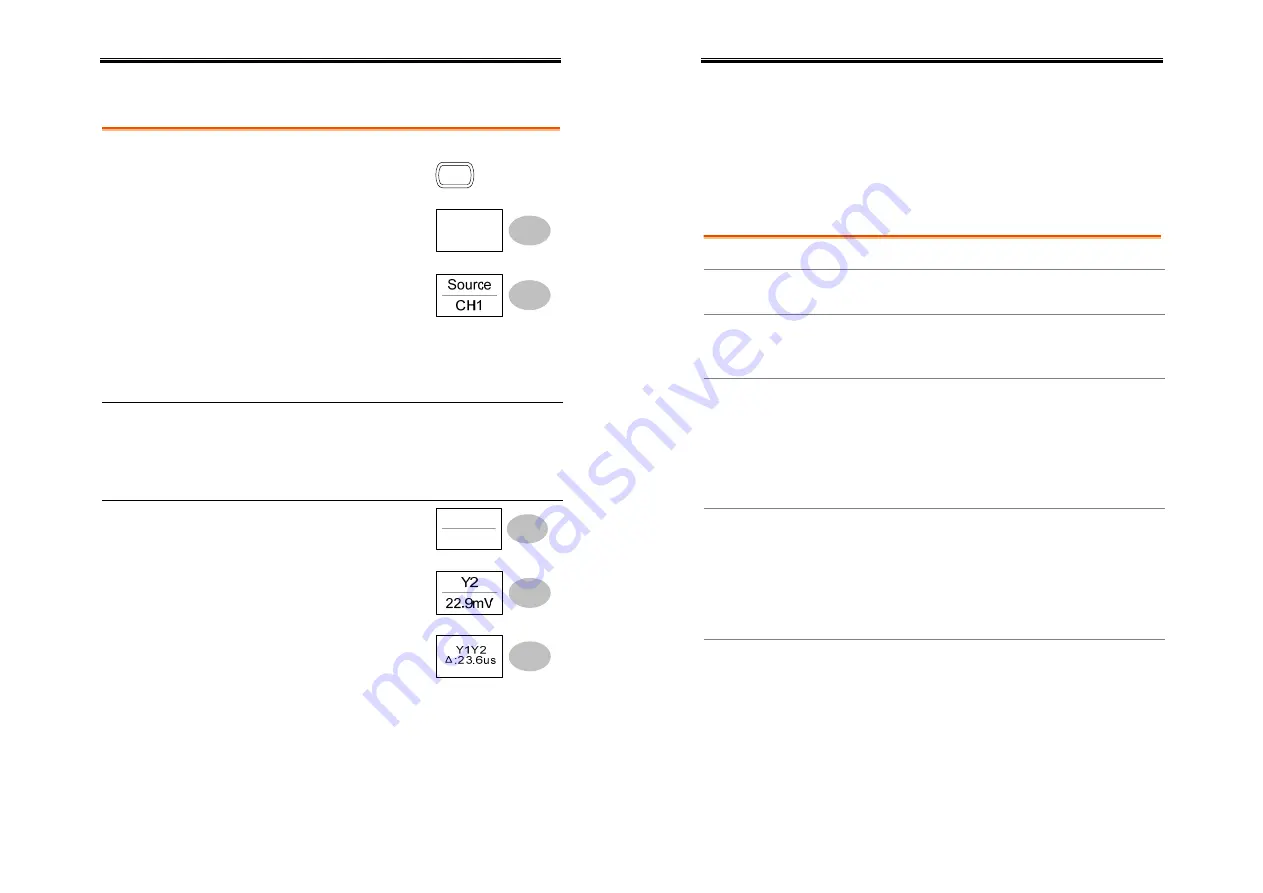
Press the Cursor key.
Cursor
2.
Press
X
↔
Y
to select the
vertical (Y1&Y2) cursor.
X
↔
Y
3.
Press
Source
repeatedly to
select the source channel.
Range
CH1, 2, Math
4.
The cursor measurement results will appear in
the menu.
Parameters Y1
Voltage level of the upper cursor
Y2
Voltage level of the lower cursor
∆
The voltage difference between the upper
and lower cursor
Moving the
vertical cursors
To move the upper cursor,
press
Y1
and then use the
Variable knob.
Y1
123.4mV
To move the lower cursor,
press
Y2
and then use the
Variable knob.
To move both cursors at once,
press
Y1Y2
and then use the
Variable knob.
User Manual – SEFRAM 53X2DC
48
Math Operations
The Math operations can add, subtract, or perform FFT on the input
waveforms. The resulted waveform can be measured using the
cursors, and saved or recalled just like normal input signals.
Overview
Addition (+)
Adds amplitude of CH1 & CH2 signals.
Subtraction (–)
Extracts the amplitude difference between CH1 &
CH2.
FFT
Runs FFT calculation on a signal. Four types of
FFT windows are available: Hanning, Flattop,
Rectangular, and Blackman.
Frequency
resolution
Good
Hanning FFT
window
Amplitude
resolution
Not good
Suitable
for....
Frequency measurement on
periodic waveforms
Frequency
resolution
Not good
Flattop FFT
window
Amplitude
resolution
Good
Suitable
for....
Amplitude measurement on
periodic waveforms
Frequency
resolution
Very good
Rectangular FFT
window
Amplitude
resolution
Bad
Suitable
for....
Single-shot phenomenon
(this mode is the same as
having no window at all)
















































