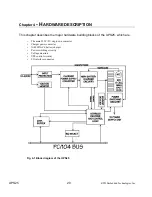
UPS25 24
RTD Embedded Technologies, Inc
Discharging can also be initiated by setting the discharge bit #1 in the control
register to a high, and bringing this bit to low again. Care must be taken not to
overheat your system since the discharged battery power is converted to heat
directly into the metal heat sink. Only discharge when the ambient temperature is
low enough, or when adequate cooling is present. In any case Ni-MH batteries do
not require as critically periodical discharging as Ni-Cd batteries do. This
procedure is recommended to do only every now and then to make sure that
battery performance in maintained. For Ni-Cd systems it is recommended to
periodically perform the discharge-before-charge to maintain good battery
performance and reduce memory effect of the Ni-Cd battery pack. Discharging
may be required if the back up is used very infrequently and for a very short
period of time.
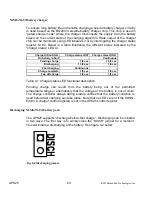
Charger mode configuration- solder blobs B2 and B3
The solder blobs shown in Figure 4-3 below let you configure the operation of the
battery charger unit and the charge algorithm. These blobs connect to GND while
the top two connections are closed and to VCC while the bottom two are closed.
Fig. 4-3 Charger configuration, solder blobs B2 and B3
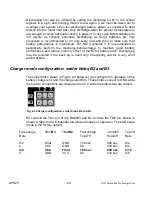
B3 controls the TM1 pin of the BQ2003 and B2 controls the TM2 pin. Below is
shown a table that will illustrate the allowed modes of operation. The bold setup
mode is the factory default.
Fast-charge
TM1/B3 TM2/B2
Fast charge
-dV/MCV
Top off
Rate Top-Off
Hold-off
Rate
C/2 Float
GND
180
sec
820
sec
Dis
C
VCC
GND
90
410
sec
Dis
C/2 VCC
Float
180
sec
820
sec
C/16
C
GND
VCC
90
410
sec
C/8