Menu Options Overview
Shown below are the menu options as they appear on the instruments display. While many of
these options are not required to operate the instrument, they have been made available to
enhance the functionality of the Mark III refractometer. To access the menu options screen,
press the key.
To select an option, press the or keys to advance to and highlight the desired option.
Press the key to enter and view the sub menu options. Using the and keys,
scroll through the option choices and press when the desired selection is highlighted.
Menu Options
- Calibrate
- Channel 1
- Sucrose
- Mode
- Index-TC
- Language
- Auto Temp. Equil.
- +/-0.04
o
C
- Password
- RS232 Baud
- Time
- Date
- Contrast
- ID
Measuring Solid Samples
The Mark III is capable of measuring transparent or translucent plastic or glass solid samples with
the upper prism raised. The instrument can also be used to measure very thin pliable solids, such
as contact lens material, that can fit between the prisms when closed.
Solid samples must be shaped and polished correctly in order to be read. The size of solid samples
should be no larger than 35mm Long x 12mm Wide x and a minimum of 2mm High. Also one side
of the sample and one of the perpendicular surfaces that will face the illumination source, must
be polished. All other sides should be frosted for best results.
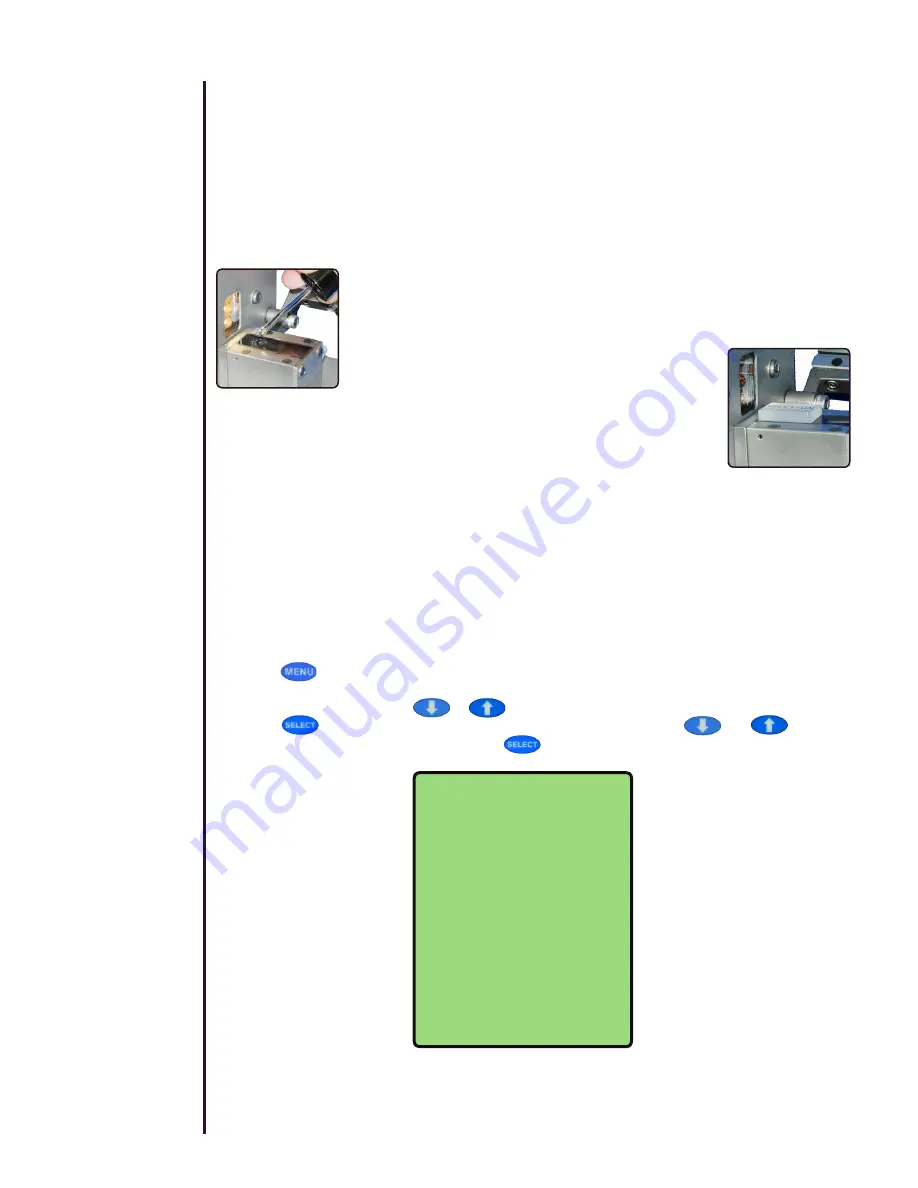
To measure a solid sample, apply a drop of a suitable contact fluid that has
a higher refractive index value than the sample being read (Fig 9). Reichert
recommends Bromonapthalene for any solid that will not be adversely affected
by this liquid.
Place the polished side of the solid sample down on the
contact fluid avoiding air bubbles from being trapped in
the process. Also place the polished perpendicular side
toward the light source of the Mark III (Fig 10).
To complete the measurement process, follow the procedure outlined in the
section “
Sample Analysis
”.
Note: Do not lower the upper illumination prism onto a solid sample as it may cause damage to
the instrument.
Fig 9
Fig 10
6


















