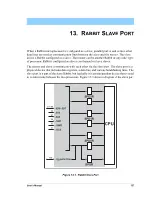
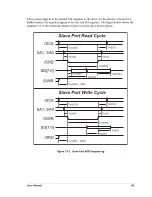
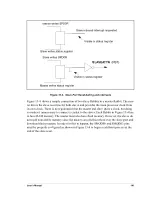
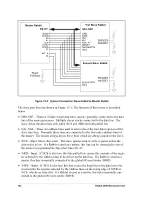
User’s Manual
147
As a simple example, suppose that the slave is to be used as a four-port UART. It has the
capability to send or receive characters on any of its four serial ports. Leaving aside the
question of setup for parameters, such as the baud rate, we could define a protocol as fol-
lows.
SPD0R readable by master is a status register with bits indicating which of the four
receivers and four transmitters is ready, that is, has a character received or is ready to
send a character.
SPD0R writable by the master is a control register used to send commands to the slave.
SPD1R is used to send or receive data characters or control bytes.
The line /SLAVEATTN is wired to the external interrupt request of the master so that
the master is interrupted when the slave writes to SPD0R. Typically the slave will
write to SPD0R when there is a change of status on one of the serial ports.
The slave can interrupt the master at any time by storing to SPD0R. It will do this every
time an enabled transmitter is ready to accept a character or every time an enabled receiver
receives a character. When it stores to SPD0R, it will store a code indicating the reason for
the interrupt, that is, receive or transmit and channel number. If the cause is receive, the
received character will also be placed in SPD1R writable by the slave. When the master is
interrupted for any reason, the master will sneak a peek at SPD0R by reading SPSR. If the
interrupt is caused by a receive character, it will remove the character from SPD1R and
read SPD0R to handshake with the slave.
If the master is interrupted for transmitter ready, as determined by the sneak peek, it will
place the outgoing character in SPD1R and write a code to SPD0R indicating transmit and
channel number. This will cause the slave to be interrupted, and the slave will take the
character and handshake by reading SPD0R. This handshake does not interrupt the master.
Summary of Contents for 2000
Page 1: ...Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor User s Manual 019 0069 041018 M...
Page 12: ...6 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 46: ...40 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 54: ...48 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 76: ...70 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 96: ...90 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 142: ...136 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 154: ...148 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 170: ...164 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 174: ...168 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 180: ...174 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 202: ...196 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 206: ...200 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...
Page 226: ......
Page 230: ...224 Rabbit 2000 Microprocessor...