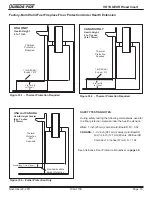
Page 34
7063-173D
November 22, 2011
R
VOYAGEUR Wood Insert
C. Calculating Alternate Floor Protection
Material
Thermal Conductivity: k value
The k value indicates the amount of heat (in BTU’s) that
will
fl ow in 1 hour through 1 square foot of a uniform mate-
rial 1 inch thick for each degree (F) of temperature differ-
ence from one side of the material to the other.
The LOWER the k factor means less heat is being con-
ducted through the non-combustible material to the com-
bustible material beneath it.
The k value of a material must be equal or smaller then the
required k value to be acceptable.
(BTU) (inch)
(foot
2
(hour) (
o
F)
Thermal Resistance: R value
The R value is a measure of a material’s resisteance
to heat transfer.
R value is convenient when more than one material is
used since you can add the R values together, where-
as you can not do this for k value.
The HIGHER the R factor means less heat is being
conducted through the non-combustible material to
the combustible material beneath it.
The R value of a material must be equal or larger then
the required R value to be acceptable.
Converting k to R:
Divide 1 by k and multiply the results times the thickness
in inches of the material.
R = 1/k x inches of thickness
Converting R to k:
Divide the inches of thickness by R.
k = inches of thickness/R
Calculatons:
Example: Floor protection requires k value of 0.84 and 3/4
inch thick.
Alternative material has a k value of 0.6 and is 3/4 inch
thick.
Divide 0.6 by .75 = k value of 0.80. This k value is smaller
than 0.84 and therefore is acceptable.