SpectraLink 8020/8030 Wireless Telephone: Administration Guide for SIP
24
PN: 1725-36038-001_N.docx
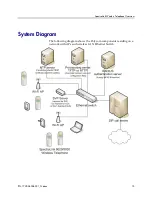
DNS
Domain Name System (DNS), an industry-standard protocol, locates
computers on an IP-based network. IP networks rely on number-
based addresses to move information on the network. However, it is
easier to remember user-friendly names than number-based
addresses, so it is necessary to translate user-friendly names into
addresses that the network can recognize. The handset can use DNS
for HTTP server IP addresses, SNMP server IP addresses, and the call
server.
Sample DHCP Server Configuration File
A sample DHCP server configuration file is illustrated below. Please
note that this is only a sample and will not work on your system as
written here. In addition, this file is specific to the ISC DHCP server.
Your configuration files must be locally programmed according to
your site requirements.
dhcpd.cfg
# /etc/dhcpd.conf
#
# Sample configuration file for ISC dhcpd
#
# Type "man dhcp-options" at prompt to get help for these options.
#
# Global parameters start at beginning of file.
# If this DHCP server is the official DHCP server for the local
# network, the authoritative directive should be uncommented.
# This means the DHCP server will send DHCPNAK messages to misconfigured
# clients.
authoritative;
# Use local address if you want the DHCP server to listen for DHCP requests
# on a specified address, rather than requests send to all addresses.
local-address 192.168.0.1;
# define the default gateway / router option 3
option routers 192.168.0.1;
# define the DNS server(s) option 6
option domain-name-servers 192.168.0.1;
# define the SYSLOG server option 7
option log-servers 192.168.0.1;
# define the domain name option 15
option domain-name "polycom.com";
# define the SVP server option code 151 as an IP address.
option svp-server code 151 = ip-address;